Chapter 13 Interfaces
ZyWALL USG 300 User’s Guide
340
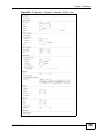
Each field is explained in the following table.
Table 75 Configuration > Network > Interface > VLAN > Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Show Advance
Settings / Hide
Advance Settings
Click this button to display a greater or lesser number of configuration
fields.
General Settings
Enable
Interface
Select this to turn this interface on. Clear this to disable this interface.
Interface
Properties
Interface
Name
This field is read-only if you are editing an existing VLAN interface.
Enter the number of the VLAN interface. You can use a number from
0~4094. See Chapter 57 on page 915 the User’s Guide for the total
number of VLANs you can configure on the ZyWALL. For example,
vlan0, vlan8, and so on.
Base Port Select the Ethernet interface on which the VLAN interface runs.
VLAN ID Enter the VLAN ID. This 12-bit number uniquely identifies each VLAN.
Allowed values are 1 - 4094. (0 and 4095 are reserved.)
Description Enter a description of this interface. It is not used elsewhere. You can
use alphanumeric and
()+/:=?!*#@$_%- characters, and it can be
up to 60 characters long.
IP Address
Assignment
Get
Automatically
Select this if this interface is a DHCP client. In this case, the DHCP
server configures the IP address, subnet mask, and gateway
automatically.
You should not select this if the interface is assigned to a VRRP group.
See Chapter 39 on page 693.
Use Fixed IP
Address
Select this if you want to specify the IP address, subnet mask, and
gateway manually.
IP Address This field is enabled if you select Use Fixed IP Address.
Enter the IP address for this interface.
Subnet Mask This field is enabled if you select Use Fixed IP Address.
Enter the subnet mask of this interface in dot decimal notation. The
subnet mask indicates what part of the IP address is the same for all
computers in the network.
Gateway This field is enabled if you select Use Fixed IP Address.
Enter the IP address of the gateway. The ZyWALL sends packets to
the gateway when it does not know how to route the packet to its
destination. The gateway should be on the same network as the
interface.