Configuring IPv6 IPv6 Overview
OmniSwitch 6600 Family Network Configuration Guide April 2006 page 15-9
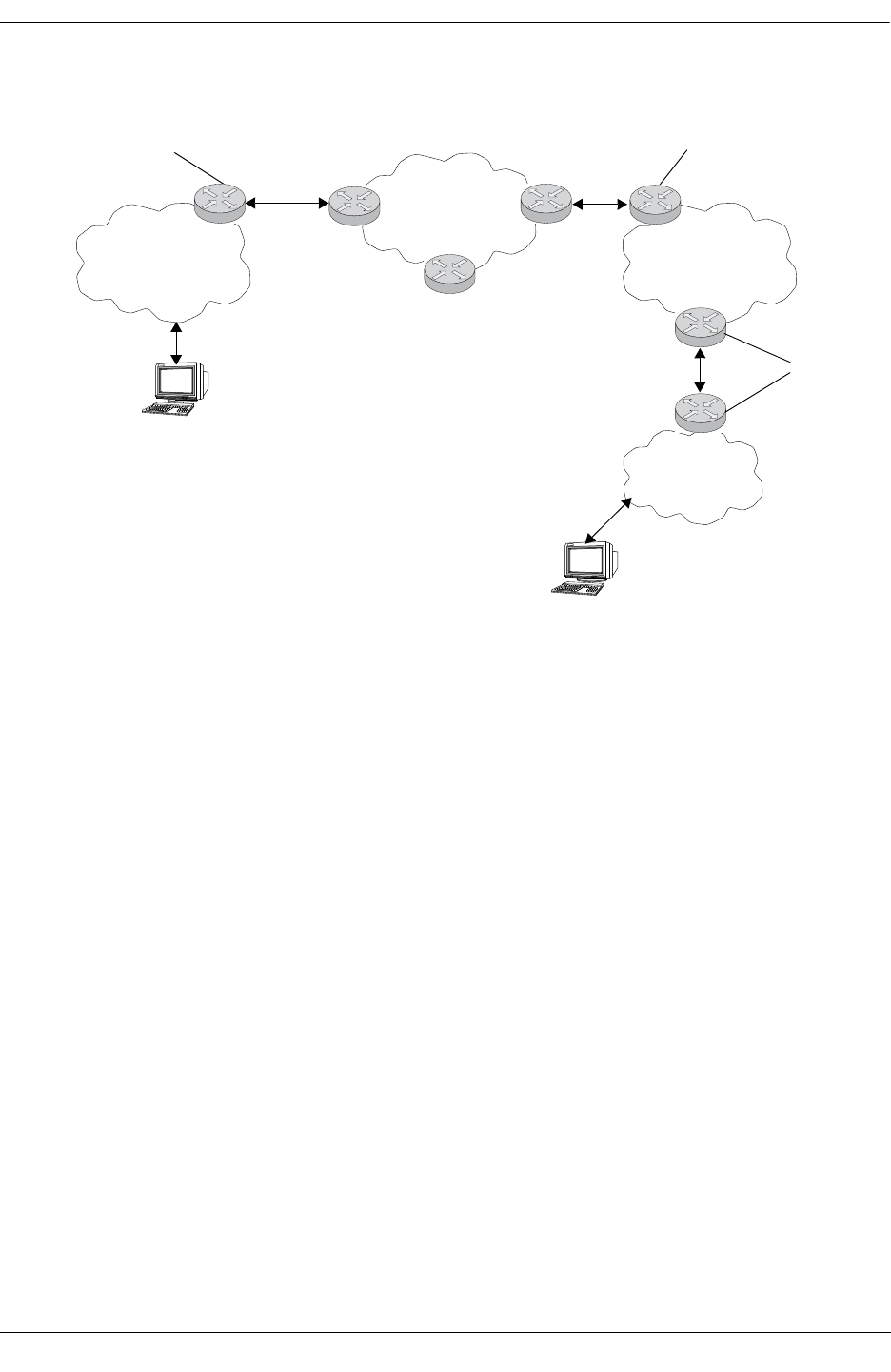
In the above diagram:
1 6to4 relay router advertises a route to 2002::/16 on its IPv6 router interface.
2 IPv6 host traffic received by the relay router that has a next hop address that matches 2002::/16 is
routed to the 6to4 tunnel interface configured on the relay router.
3 Traffic routed to the 6to4 tunnel interface is then encapsulated into IPv4 headers and sent to the desti-
nation 6to4 router over the IPv4 domain.
4 Destination 6to4 router strips IPv4 header and forwards to IPv6 destination host.
For more information about configuring an IPv6 6to4 tunnel interface, see “Configuring an IPv6 Inter-
face” on page 15-10 and “Configuring IPv6 Tunnel Interfaces” on page 15-14. For more detailed informa-
tion and scenarios using 6to4 tunnels, refer to RFC 3056.
Configured Tunnels
A configured tunnel is where the endpoint addresses are manually configured to create a point-to-point
tunnel. This type of tunnel is similar to the 6to4 tunnel in that IPv6 packets are encapsulated in IPv4 head-
ers to facilitate communication over an IPv4 network. The difference between the two types of tunnels is
that configured tunnel endpoints require manual configuration, whereas 6to4 tunneling relies on an
embedded IPv4 destination address to identify tunnel endpoints.
For more information about IPv6 configured tunnels, see “Configuring IPv6 Tunnel Interfaces” on
page 15-14. For more detailed information about configured tunnels, refer to RFC 2893. Note that RFC
2893 also discusses automatic tunnels, which are not supported with this implementation of IPv6.
IPv6 Domain
IPv4 Domain
6to4 Host
IPv6 Host
IPv6/IPv4 6to4
Relay Router
6to4 Site
IPv6 6to4
Border Router
IPv6 Site
IPv6
Router


















