286
CHAPTER 16 SERIAL INTERFACE CHANNEL 0 (
µ
PD78058F SUBSERIES)
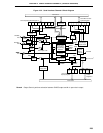
16.1 Serial Interface Channel 0 Functions
Serial interface channel 0 employs the following four modes.
• Operation stop mode
• 3-wire serial I/O mode
• SBI (serial bus interface) mode
• 2-wire serial I/O mode
Caution Do not switch the operating mode (3-wire serial I/O/ 2-wire serial I/O/SBI) while operation of serial
interface channel 0 is enabled. If switching the operation mode, first terminate the serial
operation, then carry out switching.
(1) Operation stop mode
This mode is used when serial transfer is not carried out. Power consumption can be reduced.
(2) 3-wire serial I/O mode (MSB-/LSB-first selectable)
This mode is used for 8-bit data transfer using three lines, one each for serial clock (SCK0), serial output (SO0)
and serial input (SI0). This mode enables simultaneous transmission/reception and therefore reduces the data
transfer processing time.
The start bit of transferred 8-bit data is switchable between MSB and LSB, so that devices can be connected
regardless of their start bit recognition.
This mode should be used when connecting with peripheral I/O devices or display controllers that incorporate
a conventional synchronous clocked serial interface as is the case with the 75X/XL, 78K, and 17K series.
(3) SBI (serial bus interface) mode (MSB-first)
This mode is used for 8-bit data transfer with two or more devices using two lines of serial clock (SCK0) and
serial data bus (SB0 or SB1).
The SBI mode is compatible with the NEC Serial Bus Format and sends and receives data distinguishing
between 3 different types, “Address”, “Command” and “Data”.
• Address : Data used to select a device which is the target of serial communications.
• Command : Data which gives a command to the target device.
• Data : Data which are actually transmitted.
In actual transmission, first, the master device outputs the “address” on the serial bus and selects the slave
device which is the target of the transmission from among multiple devices. After that, by transmitting
‘Commands’ and ‘Data’ between the master device and slave device, serial transmission is possible. The
receiving side can determine automatically through its hardware whether transmission data are “address”,
“command” or “data”.
This function enables the input/output ports to be used effectively and the application program serial interface
control portions to be simplified.
In this mode, the wake-up function for handshake and the output function of acknowledge and busy signals
can also be used.