Bus Controller (BC)
8-45
8.13.6 8-bit Bus in Asynchronous Mode and in Address/Data Separate Mode
8-bit bus mode is set for block 0 by setting the mode through the MMOD1 and 0 pins and the EXMOD1 and 0 pins,
and for blocks 1 to 3 by setting the BnBW bit to “0” in the corresponding memory control register. In 8-bit bus
mode, half-word access (16 bits) is performed by means of two external accesses, with A[0] = "0" for the low-order
byte and A[0] = "1" for the high-order byte. Word access (32 bits) is performed by means of four accesses, with
A[1:0] = "00", A[1:0] = "01", A[1:0] = "10", and A[1:0] = "11", starting from the low-order side. Note that the low-
order 8 bits (D7 to 0) are used for the data bus.
Asynchronous mode is used for accessing external memory at high speed; the address signals, CS signals, etc., are
output asynchronously with SYSCLK but in synchronization with the internal MCLK. In asynchronous mode,
accesses are all by fixed wait insertion.
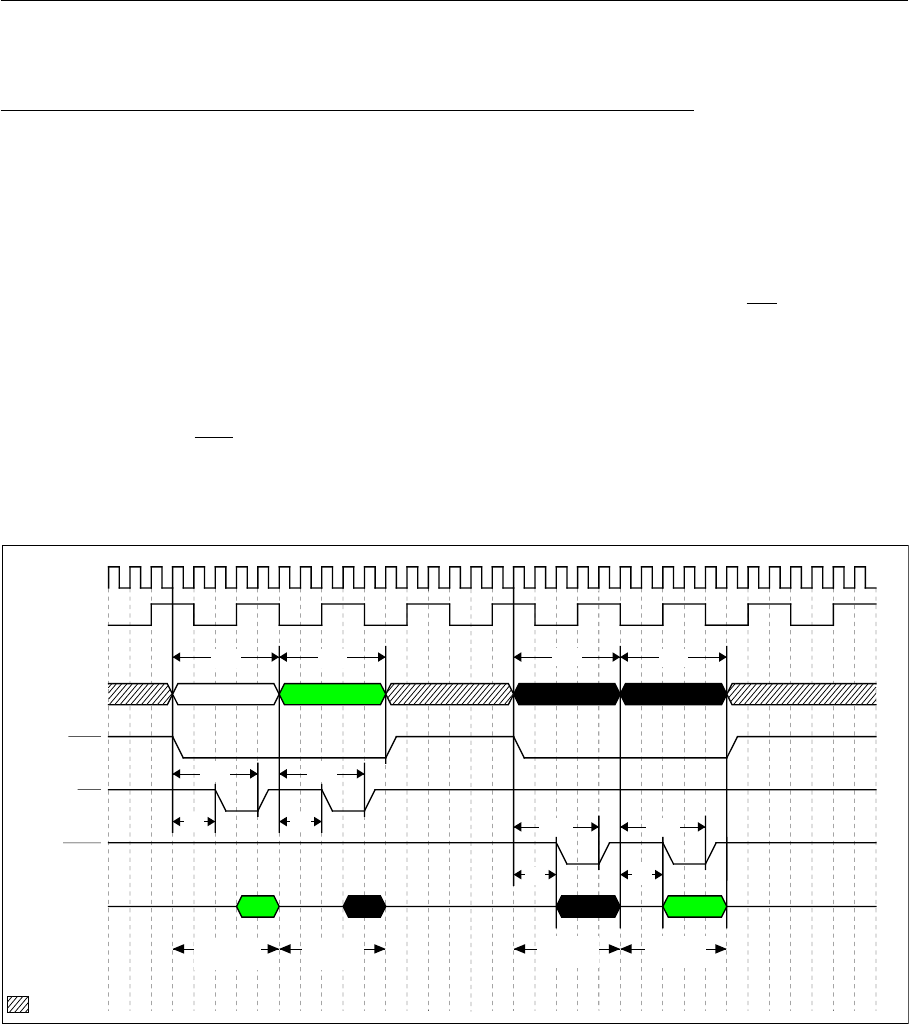
Fig. 8-13-16 is the timing chart in the case of a half-word access using an “8-bit bus in asynchronous mode, in
address/data separate mode.”
Note that when writing, WE0 is asserted and the data is output on D7 to 0.
Fig. 8-13-16 Access Timing on a 8-bit Bus, in Asynchronous Mode and in
Address/Data Separate Mode (MCLK = SYSCLK multiplied by 4)
For details on the various timing settings, refer to the description of the memory control register in section 8.6,
“Description of Registers.”
Note: For details on the mode settings, refer to Table 8-9-1, “Mode Settings by the BC External Pins.”
An
D7-0
WE0
RE
CSn
EA
MCLK
SYSCLK
REN
A[0]=0
A[0]=1
A[0]=0
A[0]=1
EA
REN
EA
WEN
EA
WEN
Read low-
order side
Read high-
order side
Write low-
order side
Write high-
order side
BCE BCE
BCE
BCE
: Undefined


















