16 AMD Geode™ LX Processors Data Book
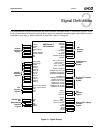
Architecture Overview
33234H
2.1.2 Memory Management Unit
The memory management unit (MMU) translates the linear
address supplied by the integer unit into a physical address
to be used by the cache unit and the internal bus interface
unit. Memory management procedures are x86-compati-
ble, adhering to standard paging mechanisms.
The MMU also contains a load/store unit that is responsible
for scheduling cache and external memory accesses. The
load/store unit incorporates two performance-enhancing
features:
• Load-store reordering gives memory reads required by
the integer unit a priority over writes to external memory.
• Memory-read bypassing eliminates unnecessary
memory reads by using valid data from the execution
unit.
2.1.3 Cache and TLB Subsystem
The cache and TLB subsystem of the CPU Core supplies
the integer pipeline with instructions, data, and translated
addresses (when necessary). To support the efficient deliv-
ery of instructions, the cache and TLB subsystem has a
single clock access 64 KB 16-way set associative instruc-
tion cache and a 16-entry fully associative TLB. The TLB
performs necessary address translations when in protected
mode. For data, there is a 64 KB 16-way set associative
writeback cache, and a 16-entry fully associative TLB.
When there is a miss to the instruction or data TLBs, there
is a second level unified (instruction and data) 64-entry 2-
way set associative TLB that takes an additional clock to
access. When there is a miss to the instruction or data
caches or the TLB, the access must go to the GeodeLink
Memory Controller (GLMC) for processing. Having both an
instruction and a data cache and their associated TLBs
improves overall efficiency of the integer unit by enabling
simultaneous access to both caches.
The L1 caches are supported by a 128 KB unified L2 victim
cache. The L2 cache can be configured to hold data,
instructions, or both. The L2 cache is 4-way set associa-
tive.
2.1.4 Bus Controller Unit
The bus controller unit provides a bridge from the proces-
sor to the GLIUs. When external memory access is
required, due to a cache miss, the physical address is
passed to the bus controller unit, that translates the cycle
to a GeodeLink cycle.
2.1.5 Floating Point Unit
The Floating Point Unit (FPU) is a pipelined arithmetic unit
that performs floating point operations as per the IEEE 754
standard. The instruction sets supported are x87, MMX,
and AMD 3DNow! technology. The FPU is a pipelined
machine with dynamic scheduling of instructions to mini-
mize stalls due to data dependencies. It performs out of
order execution and register renaming. It is designed to
support an instruction issue rate of one per clock from the
integer core. The datapath is optimized for single precision
arithmetic. Extended precision instructions are handled in
microcode and require multiple passes through the pipe-
line. There is an execution pipeline and a load/store pipe-
line. This allows load/store operations to execute in parallel
with arithmetic instructions.
2.2 GeodeLink™ Control Processor
The GeodeLink Control Processor (GLCP) is responsible
for reset control, macro clock management, and debug
support provided in the Geode LX processor. It contains
the JTAG interface and the scan chain control logic. It sup-
ports chip reset, including initial PLL control and program-
ming and runtime power management macro clock control.
The JTAG support includes a TAP Controller that is IEEE
1149.1 compliant. CPU control can be obtained through
the JTAG interface into the TAP Controller, and all internal
registers, including CPU Core registers, can be accessed.
In-circuit emulation (ICE) capabilities are supported
through this JTAG and TAP Controller interface.
The GLCP also includes the companion device interface.
The companion device has several unique signals con-
nected to this module that support Geode LX processor
reset, interrupts, and system power management.
2.3 GeodeLink™ Interface Units
Together, the two GeodeLink Interface Units (GLIU0 and
GLIU1) make up the internal bus derived from the
GeodeLink architecture. GLIU0 connects five high band-
width modules together with a seventh link to GLIU1 that
connects to the five low bandwidth modules.
2.4 GeodeLink™ Memory Controller
The GeodeLink Memory Controller (GLMC) is the source
for all memory needs in a typical Geode LX processor sys-
tem. The GLMC supports a memory data bus width of 64
bits and supports 200 MHz, 400 MT/S for DDR (Double
Data Rate).
The modules that need memory are the CPU Core, Graph-
ics Processor, Display Controller, Video Input Port, and
Security Block. Because the GLMC supports memory
needs for both the CPU Core and the display subsystem,
the GLMC is classically called a UMA (Unified Memory
Architecture) subsystem. PCI accesses to main memory
are also supported.
Up to four banks, with eight devices maximum in each bank
of SDRAM, are supported with up to 512 MB in each bank.
Four banks means that one or two DIMM or SODIMM mod-
ules can be used in a AMD Geode LX processor system.
Some memory configurations have additional restrictions
on maximum device quantity.