Two Port 10/100 Managed Ethernet Switch with 16-Bit Non-PCI CPU Interface
Datasheet
Revision 1.4 (08-19-08) 86 SMSC LAN9311/LAN9311i
DATASHEET
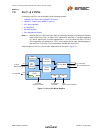
7.2.1.3 Scrambler and PISO
Repeated data patterns (especially the IDLE code-group) can have power spectral densities with large
narrow-band peaks. Scrambling the data helps eliminate these peaks and spread the signal power
more uniformly over the entire channel bandwidth. This uniform spectral density is required by FCC
regulations to prevent excessive EMI from being radiated by the physical wiring. The scrambler also
performs the Parallel In Serial Out conversion (PISO) of the data.
The seed for the scrambler is generated from the PHY address, ensuring that each PHY will have its
own scrambler sequence. For more information on PHY addressing, refer to Section 7.1.1, "PHY
Addressing".
7.2.1.4 NRZI and MLT-3 Encoding
The scrambler block passes the 5-bit wide parallel data to the NRZI converter where it becomes a
serial 125MHz NRZI data stream. The NRZI is then encoded to MLT-3. MLT-3 is a tri-level code where
a change in the logic level represents a code bit “1” and the logic output remaining at the same level
represents a code bit “0”.
7.2.1.5 100M Transmit Driver
The MLT-3 data is then passed to the analog transmitter, which drives the differential MLT-3 signal on
output pins TXPx and TXNx (where “x” is replaced with “1” for the Port 1 PHY, or “2” for the Port 2
PHY), to the twisted pair media across a 1:1 ratio isolation transformer. The 10BASE-T and 100BASE-
TX signals pass through the same transformer so that common “magnetics” can be used for both. The
transmitter drives into the 100
Ω impedance of the CAT-5 cable. Cable termination and impedance
matching require external components.
7.2.1.6 100M Phase Lock Loop (PLL)
The 100M PLL locks onto the reference clock and generates the 125MHz clock used to drive the 125
MHz logic and the 100BASE-TX Transmitter.
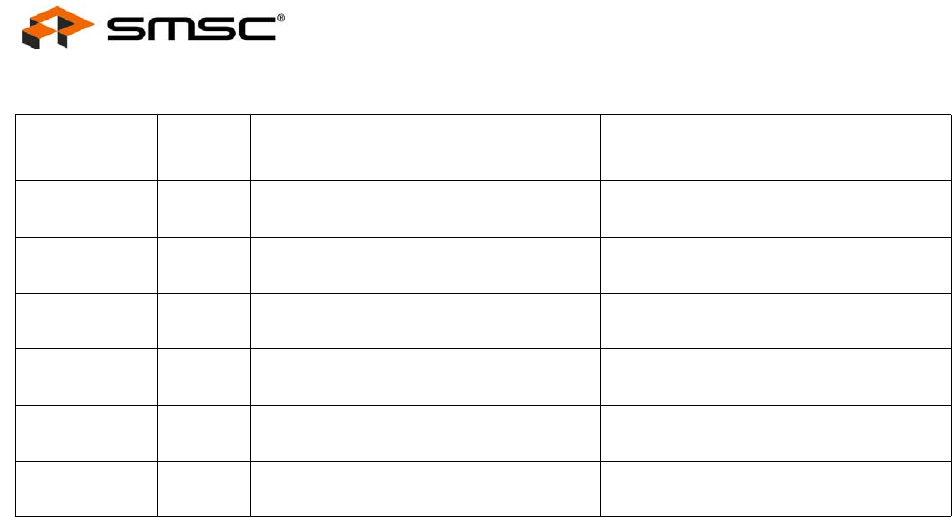
00010 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
00011 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
00101 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
01000 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
01100 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
10000 /V/ INVALID, MII Receive Error (RXER) if
during MII Receive Data Valid (RXDV)
INVALID
Table 7.2 4B/5B Code Table (continued)
CODE
GROUP SYM
RECEIVER
INTERPRETATION
TRANSMITTER
INTERPRETATION