Intel
®
820E Chipset
R
Design Guide 145
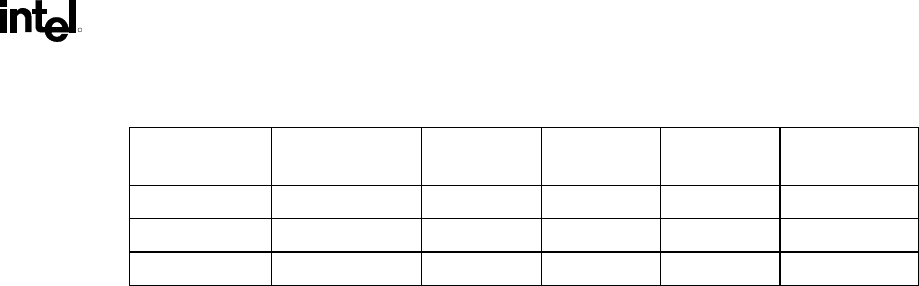
Table 53. Example T
FLT_MIN
Calculations
1
(Frequency Independent)
Driver Receiver THOLD ClkSKEW TCO_MIN Recommended
TFLT_MIN
Processor
2
Processor
2
0.8 0.2 -0.1 1.2
Processor
2
Intel
®
82820 MCH 0.28 0.2 -0.1 .58
82820 MCH Processor
2
0.8 0.2 0.5 .5
NOTES:
1. All times in nanoseconds.
2. Processor values specified in this table are examples only. Refer to the appropriate processor datasheet for the
specification values.
3.2.2. Determine the Desired General Topology, Layout, and Routing
After calculating the timing budget, determine the approximate location of the processor and the chipset
on the baseboard (see Section 2.10).
3.2.3. Pre-Layout Simulation
3.2.3.1. Methodology
Analog simulations are recommended for high-speed system bus designs. Start simulations prior to
layout. Pre-layout simulations provide a detailed picture of the working “solution space” that satisfies the
flight time and signal quality requirements. The layout recommendations in the previous sections are
based on pre-layout simulations conducted at Intel. By basing board layout guidelines on the solution
space, the iterations between layout and post-layout simulation can be reduced.
Intel recommends running simulations at the device pads for signal quality and at the device pins for
timing analysis. However, simulation results at the device pins may later be used to correlate simulation
performance against actual system measurements.
3.2.3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
Pre-layout analysis includes a sensitivity analysis using parametric sweeps. Parametric sweep analysis
involves varying one or two system parameters while all others (e.g., driver strength, package, Z
0
, S
0
) are
held constant. This allows the sensitivity of the proposed bus topology to varying parameters to be
analyzed systematically. Sensitivity of the bus to minimum flight time, maximum flight time, and signal
quality should be covered. Suggested sweep parameters include trace lengths, termination resistor values,
and any other factors that may affect the flight time, signal quality, and feasibility of layout. Minimum
flight time and worst signal quality are typically analyzed using fast I/O buffers and interconnect.
Maximum flight time is typically analyzed using slow I/O buffers and slow interconnects.
Outputs from each sweep should be analyzed to determine which regions meet timing and signal quality
specifications. To establish the working solution space, find the common space across all sweeps that
pass timing and signal quality tests. The solution space should allow enough design flexibility for a
feasible, cost-effective layout.


















