Intel
®
820E Chipset
R
Design Guide 81
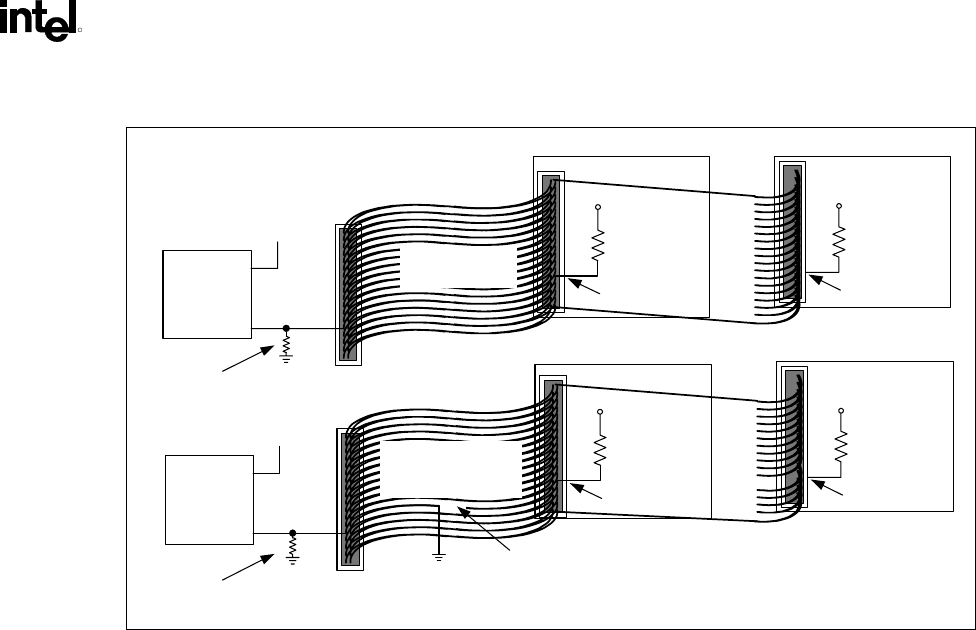
Figure 46. Combination Host-Side/Device-Side IDE Cable Detection
80-conductor
IDE cable
IDE drive
5 V
ICH2
GPIO
GPIO
Open
IDE drive
5 V
40-conductor
cable
IDE drive
5 V
PDIAG#
ICH2
GPIO
GPIO
IDE drive
5 V
Resistor required for
non-5V-tolerant GPI.
PDIAG#
PDIAG#PDIAG#
Resistor required for
non-5V-tolerant GPI.
10 k
Ω
10 k
Ω
To secondary
IDE connector
To secondary
IDE connector
PDIAG#/
CBLID#
PDIAG#/
CBLID#
10 k
Ω
10 k
Ω
10 k
Ω
10 k
Ω
IDE_combo_cable_det
After diagnostics, this mechanism allows the BIOS to sample PDIAG#/CBLID#. If the signal is high,
there is a 40-conductor cable in the system and ATA modes 3, 4 and 5 must not be enabled.
If PDIAG#/CBLID# is detected low, then there may be an 80-conductor cable in the system, or there
may be a 40-conductor cable and a legacy slave device (Device 1) that does not release the
PDIAG#/CBLID# signal as required by the ATA/ATAPI-4 standard. In this case, BIOS should check the
IDENTIFY DEVICE information in a connected device that supports Ultra DMA modes higher than 2. If
ID Word 93 bit 13 is 1, then an 80-conductor cable is present. If this bit is 0, then a legacy slave (Device
1) is preventing proper cable detection, and the BIOS should configure the system as though a
40-conductor cable were present and notify the user of the problem.


















