12-3
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Software Configuration Guide
OL-16506-17
Chapter 12 IEEE 1588v2 PTP Support
Information About IEEE 1588v2 PTP
• Grand Master--An IEEE1588v2 PTP network needs a grand master to provide a precise time
source. The most economical way of obtaining the precise time source for the grand master is
through a Global Positioning System (GPS) because it provides +/- 100 nanosecond (ns) accuracy.
First, the PTP grand master’s built-in GPS receiver converts the GPS timing information to PTP time
information, which is typically Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), and then delivers the UTC time
to all the PTP clients.
• PTP client--A PTP client has to be installed on servers, network-monitoring and
performance-analysis devices, or other devices that want to use the precise timing information
provided by PTP, and it’s mostly an ordinary clock. The two kinds of PTP clients are pure software
PTP clients and hardware-assistant PTP clients.
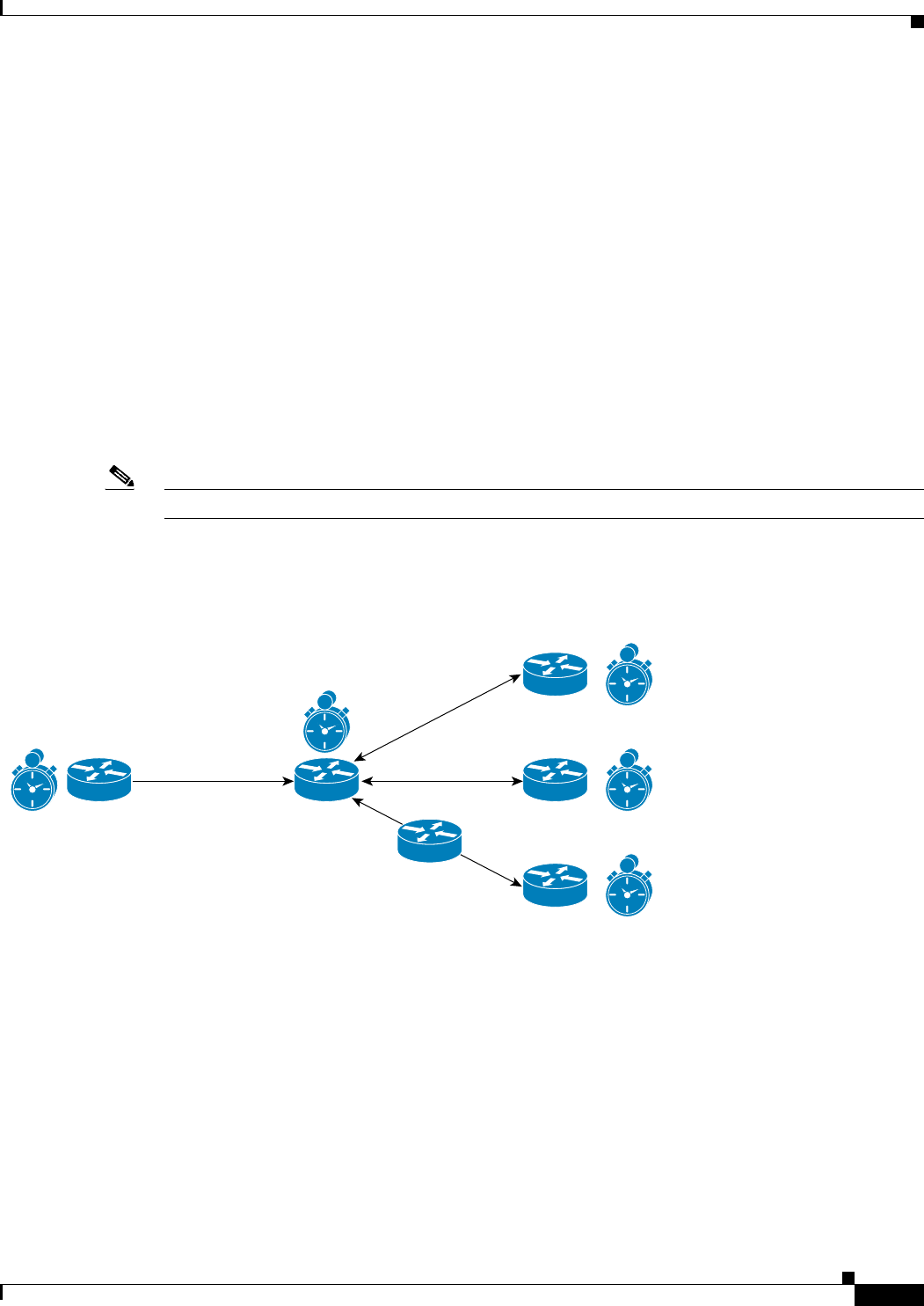
• PTP boundary clock--Any router that is between a PTP master and PTP slave can act as a PTP
boundary clock router. It has two interfaces, one facing the PTP master and another facing the PTP
slave. The boundary clock router acts as a slave on the interface facing the PTP master router, and
acts as a master on the interface facing the PTP slave router. The PTP boundary clock router is
deployed to minimize timing delay in cases where the distance between PTP master router and the
PTP slave router is more.
Note Intermediary nodes between PTP master and slave should be a PTP-enabled or transparent clock node.
Figure 12-1 shows the functions of a PTP Enabled device.
Figure 12-1 Functions of a PTP-Enabled Device
Clock-Synchronization Process
Clock synchronization is achieved through a series of messages exchanged between the master clock and
the slave clock as shown in Figure 12-2.
PTP Master
M - Master Port
S - Slave Port
PTP TC
PTP Boundary
PTP Slaves
S
SMSM
M
M
S
372860


















