12-5
Cisco ASR 1000 Series Aggregation Services Routers Software Configuration Guide
OL-16506-17
Chapter 12 IEEE 1588v2 PTP Support
Information About IEEE 1588v2 PTP
PTP Clocking Modes
The following are the PTP clocking modes supported on a Cisco ASR 1002-X Router:
• Unicast Mode--In unicast mode, the master sends the Sync or Delay_Resp messages to the slave on
the unicast IP address of the slave, and the slave in turn sends the Delay_Req message to the master
on the unicast IP address of the master.
• Unicast Negotiation Mode--In unicast negotiation mode, the master does not know of any slave
until the slave sends a negotiation message to the master. The unicast negotiation mode is good for
scalability purpose because one master can have multiple slaves.
PTP Accuracy
Accuracy is an important aspect of PTP implementation on an Ethernet port. For a packet network,
Packet Delay Variation (PDV) is one of the key factors that impacts the accuracy of a PTP clock. The
Cisco ASR 1002-X Router can handle the PDV of the network with its advanced hardware and software
capabilities, such as hardware stamping and special high-priority queue for PTP packets. It can provide
around 300 ns accuracy in a scalable deployment scenario.
The two methods used on the same topology to cross-check and verify the results are:
• One-pulse-per-second (1PPS) to verify the PTP slave.
• Maximum Time Interval Error (MTIE) and Time Deviation (TDEV) to verify the PDV.
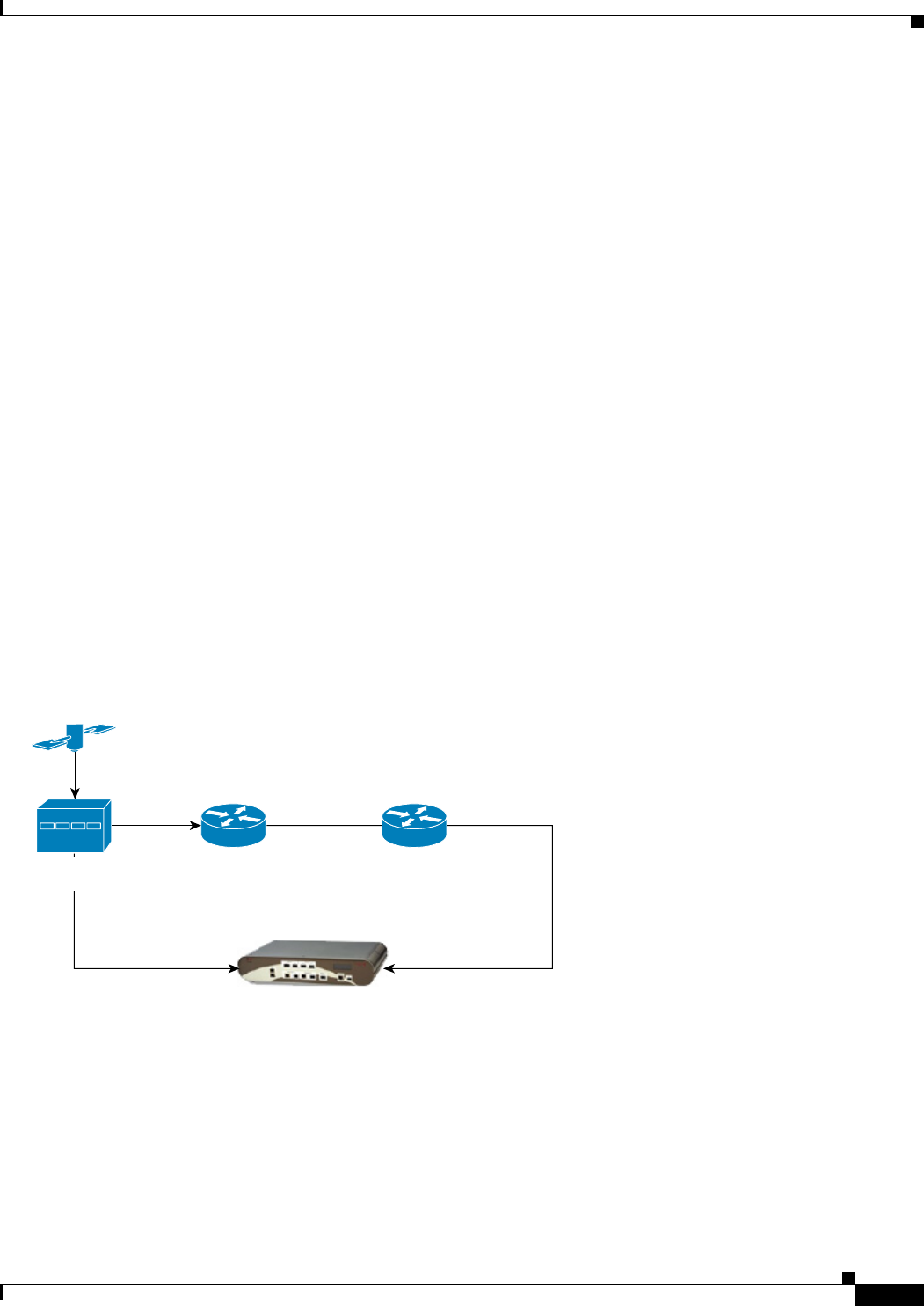
The verification topology includes a grand master with a GPS receiver, a Cisco ASR 1002-X Router, PTP
hardware slave clocks with 1PPS output, and a test equipment for the measurement.
Figure 12-3 1PPS Accuracy Measurement
ToD + 1pps
1pps reference
Clanex - Paragon X
1pps measurement
PTP SlavePTP Master
Gige link
PTP Grandmaster
with GPSreceiver
372861
