Avaya P550R, P580, P880, and P882 Multiservice Switch User Guide, v5.3.1 5-5
Configuring Port Parameters
* Note: If a Gigabit module that does not support the
autonegotiation is connected to a device that does,
disable autonegotiation to ensure proper operation.
If you enable flow control, the switch manages the inbound buffers
with flow control (IEEE 802.1X XOFF, or Backpressure) applied
when a high water mark is reached. Thus, no matter which flow
control option is chosen, outgoing pauses or backpressure are only
applied to the port on which the parameter is set based upon the
inbound traffic for that port in the default queuing mode.
Flow control is not applied across the switch itself. Therefore, if you
have a server sending data on one port at 100MB and a client
receiving the data at 10MB, the switch will not throttle the data at
the Server’s input based on outgoing buffer backup on the client’s
port in this default queuing mode.
Switch Port Features
The Avaya P550R/P580/P880/P882 Multiservice switches all
support up to 1000 VLANs and also supports multiple forwarding
databases. This means that each VLAN is associated with its own
Address Forwarding Table (AFT). Therefore, identical MAC
addresses can simultaneously exist on multiple VLANs. The Avaya
Multiservice switches provide parameters for configuring VLAN/port
associations.
This section provides the following:
■ Relationship Between Different Switch Port Parameters
■ Assigning VLANs to a Port and Associated Issues
■ Setting the Port VLAN attribute in the Switch Port
Configuration dialog box. This identifies the VLAN to which
all untagged frames received on the port are classified. Note
that a port has exactly one Port VLAN. Changing this to a
new VLAN removes the port from the old VLAN.
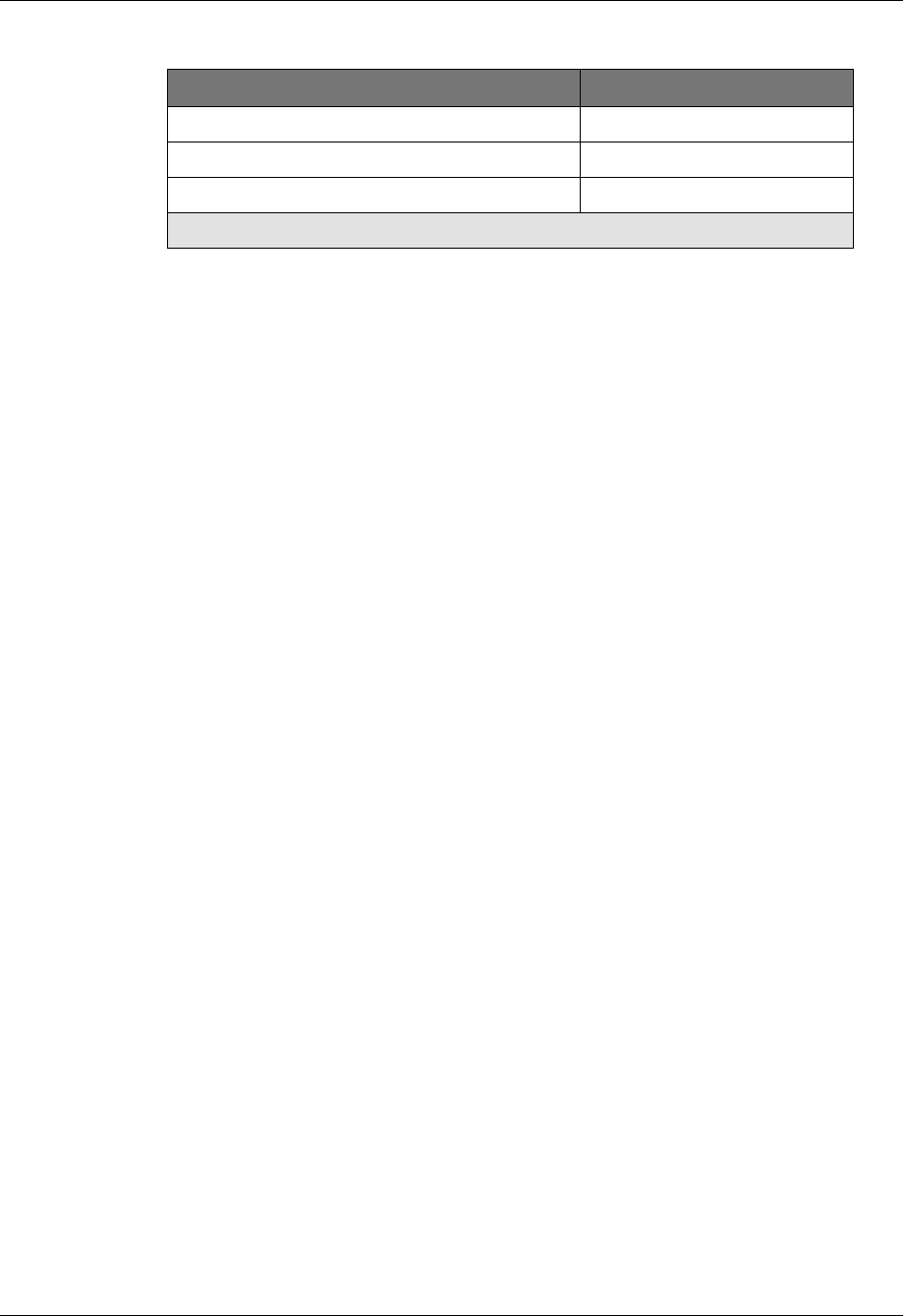
M5502R-1000SX-F J or earlier
M5502R-1000LX-F J or earlier
M5502R-1000SLX-F H or earlier
Table 5-1. Gigabit Modules not Supporting Autonegotiation
Gigabit Module Model Number Hardware Revision
2 of 2


















