210 IBM System Storage DS6000 Series: Copy Services with IBM System z
corresponds to the sectors that were updated since the last volume bitmap scan was
done. These are the out-of-sync sectors.
Because of the bitmap scan method, writes might not be applied on to the secondary
volume in the same sequence as they are written to the primary volume.
When terminating the Global Copy relationship to establish host access to secondary
volumes, the first issue might cause you to lose transactions. Since a file system or database
consistency depends on the correct ordering of write sequences, the second issue might
cause inconsistent volumes. Therefore, to use secondary volumes by the host systems, you
must make them
point-in-time consistent:
The application must be quiesced and the volume pairs temporarily suspended. This is
necessary for ensuring consistency not only at the volume level, but also at the application
level.
The secondary volumes have to
catch-up to their primary counterparts. Global Copy
catch-up is the name of the transition that occurs to a Global Copy pair when it goes from
its normal out-of-sync condition until it reaches a full sync condition. At the end of this
transition, the primary and secondary volumes become fully synchronized.
A FlashCopy of the secondary volumes onto tertiary volumes should now be performed,
followed by resuming the Global Copy pairs.
These tertiary volumes are then a consistent point-in-time copy of the primary volumes.
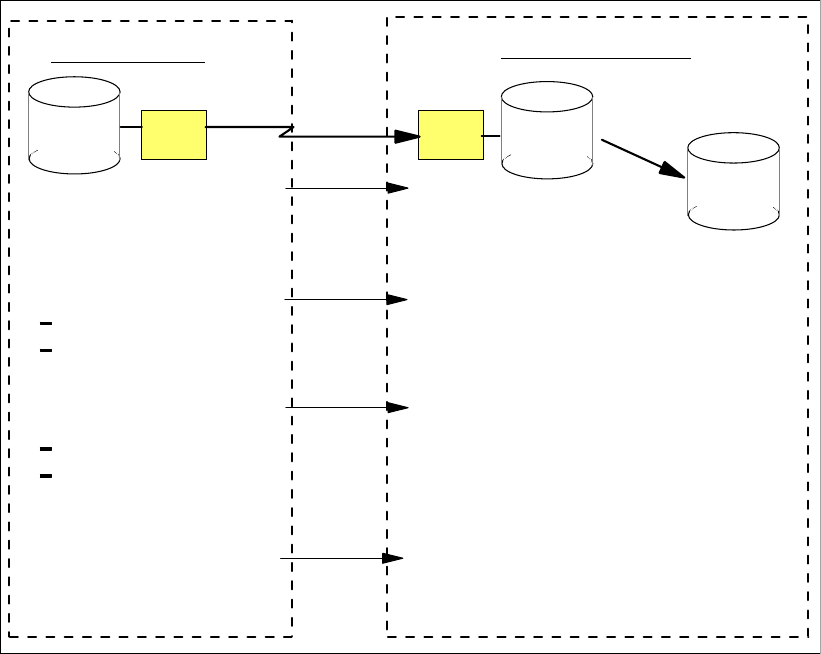
Figure 18-3 illustrates a procedure to get a consistent point-in-time copy at the secondary
site.
Figure 18-3 Create a Global Copy consistent copy
channel
extender
channel
extender
F
l
a
s
h
C
o
p
y
secondary
tertiary
primary
non-synchronous
copy
over long distance
5. FlashCopy
6. Reestablish suspended
pairs (resync)
consistent tertiary
copy of data
Secondary Site
Primary Site
minimum performance impact fuzzy copy of data
1. Quiesce application
updates
2. Catch-up (synchronize
volume pairs)
go-to-sync / suspend
or wait for application
writes to quiesce
3. Build consistency on
recovery data
resync and freeze
or freeze (suspend)
4. Resume application writes
as soon as freeze is done
individual volume pairs synchronize
copy of data consistent across
volume pairs