256 IBM System Storage DS6000 Series: Copy Services with IBM System z
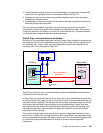
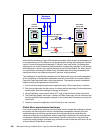
Figure 22-10 Establish Global Copy connectivity between both sites
Note in Figure 22-10that we establish Global Copy paths over an existing network. This
network may be based on a FCP transport technology or on an IP based network.
Global Copy paths are logical connections that are defined over the physical links that
interconnect both sites. Note that all remote mirror and copy paths (that is Metro Mirror,
Global Copy, and Global Mirror paths) are similar and are based on FCP. The term Global
Copy path just denotes that the path is intended for Global Copy use.
22.3.3 Create Global Copy relationship between local and remote volume
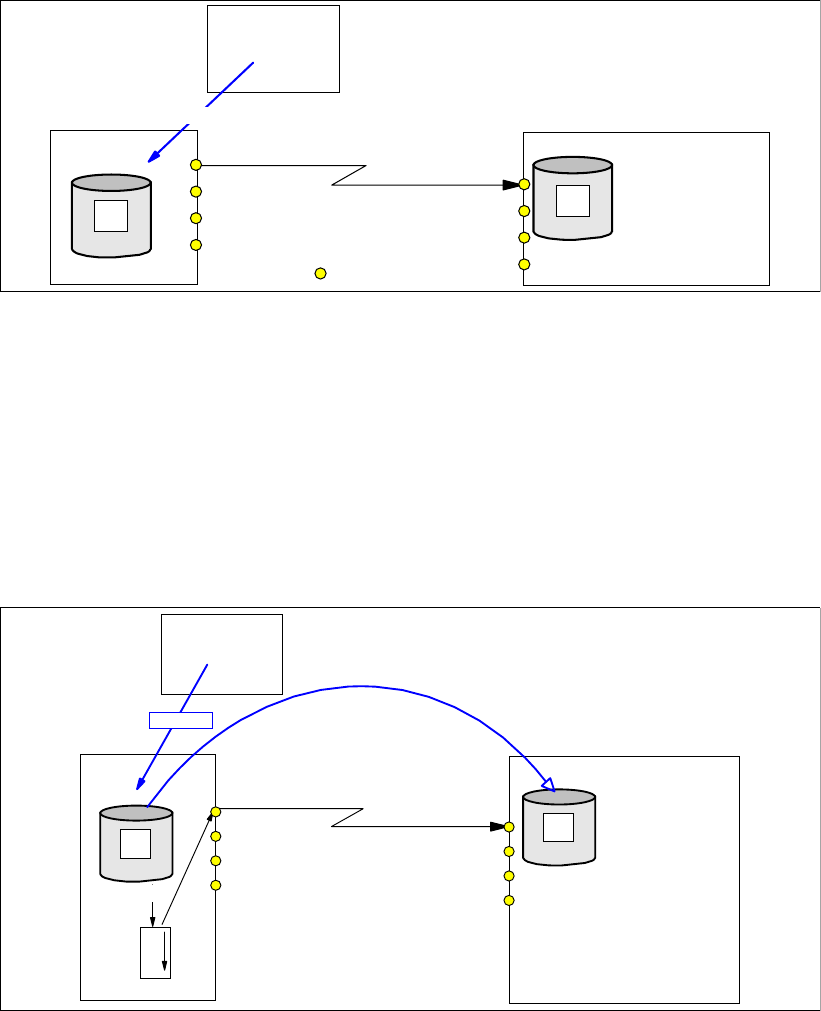
Figure 22-11 Establish Global Copy volume pair
Next, we create a Global Copy relationship between the local, or primary, volume and the
remote, or secondary, volume; see Figure 22-11. This step changes the secondary volume
state from
simplex to copy pending. This copy pending state applies to both volumes, primary
pending
and secondary pending. At the same time data starts to be copied from the primary
volume to the secondary volume. After a first complete pass through the entire A volume,
Global Copy will constantly scan through the out-of-sync bit map. This bitmap indicates
changed data as it arrives from the applications to the primary disk subsystem—Global Copy
replicates the data from the A volume to the B volume based on this out-of-sync bit map.
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
A
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
Host
Write I/O
Remote site
Local site
B
Global Copy path
FCP port
Global Copy
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
A
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
B
O
O
S
Host
Remote site
Local site
Secondary
PENDING
PENDING
Write I/O
OOS: Out-of-sync bit map
Primary