Chapter 30. IIBM TotalStorage Rapid Data Recovery 461
Figure 30-3 Dependent write protection of database integrity
Freeze is a command available through DS Command-Line Interface, DS Storage Manager
(Graphical User Interface), the ESS API, ICKDSF or TSO, that stops the write activity on all of
the active Remote Copy primary and secondary volumes of a given source and target Logical
Subsystem (LSS) pair. This function ensures consistency between the primary and
secondary volumes and can affect any LSS volumes that are in an active Remote Copy state
between the frozen LSS pair: duplex, duplex pending SYNC or duplex pending XD states. It
does not affect the suspended and simplex volumes that may be in the LSS.
The freeze operation has three effects:
1. The paths that connect the pair of LSSs being frozen are terminated.
2. The active volumes under the frozen LSS pair are suspended. This state transition, to
suspended, is then communicated to the host with alert messages. These alert messages
can be used by automation routines to trigger other recovery operations.
3. If the consistency group option was enabled at path definition time, then the ELB or SCSI
Queue Full condition is instigated, so that the write activity to the primary LSS is
temporarily queued. During this interval, other automated operations can be triggered;
such as, freezing other application-related LSS pairs.
When using freeze through DS Storage Manager (Graphical User Interface) or ICKDSF, it will
take effect on each LSS individually. This is useful for creating a point-in-time copy of the
data, but because of slight delays between the issuing of each iteration of the freeze
command it is unsuitable for preventing rolling disasters and should be done at periods of low
utilization to ensure the of the secondary data can be used.
When Remote Copy is used in conjunction with automation, such as the Geographically
Dispersed Parallel Sysplex (GDPS) or enterprise Remote Copy Management Facility
(eRCMF) service offerings from IBM Global Services, a freeze command can be
simultaneously issued to all LSSs within the configuration. This ensures globally consistent
data across all LSSs in the secondary copy of data during a disaster.
Y
M
C
Y
M
C
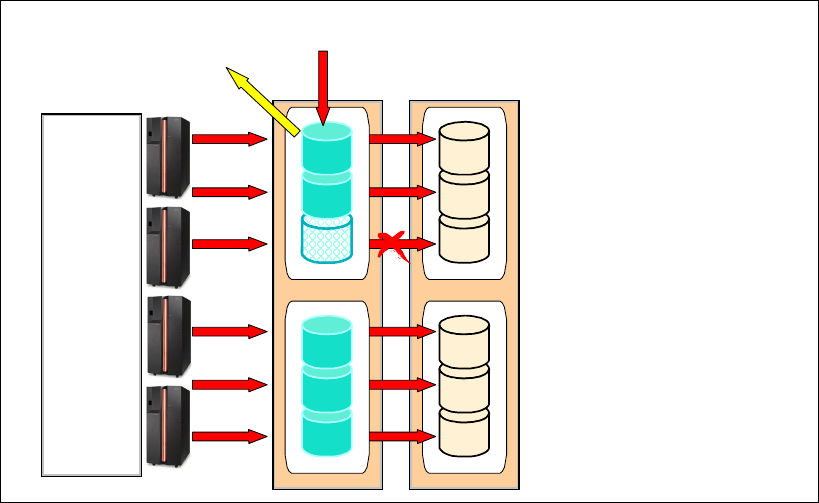
Consistency Group
control function
1. Mirroring failure
2. ESS suspends affected primary
and holds application I/O (SCSI
Queue full condition)
3.
ESS sends a notification about
the failure
4. A program like eRCMF can
receive the SNMP trap and issue
the freeze to all LSSs in the
Consistency Group
5.
ESS releases I/O if told to do so
or after PPRC Consistency
Group time out is over
Database
Application
X
L
B
X
L
B
SNMP trap
