Chapter 22. Global Mirror overview 255
When the Master and Subordinate are in a single storage disk subsystem the Subordinate is
internally managed by the Master. With two or more storage disk subsystems at the local site,
which participate in a Global Mirror session, the Subordinate is external and needs separate
attention when creating and managing a Global Mirror session or environment.
The following sections explain how Global Mirror works and how Global Mirror ensures
consistent data at any time at the remote site. First we go through the process of how to
create a Global Mirror environment. At the same time, this explanation, gives us a first insight
on how Global Mirror works.
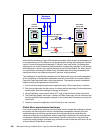
22.3 Set up a Global Mirror session
Global Mirror, as a long distance remote copy solution, is based on an efficient combination of
Global Copy and FlashCopy functions. It is the microcode that provides, from the user
perspective, a transparent and autonomic mechanism to intelligently utilize Global Copy in
conjunction with certain FlashCopy operations to attain consistent data at the remote site.
In order to understand how Global Mirror works, we start explaining first how a Global Mirror
environment, that is a Global Mirror session, is created and started. This is a step-by-step
approach and helps to understand further the Global Mirror operational aspects.
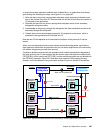
22.3.1 Simple configuration to start
In order to understand each step and to show the principles, we start with a simple application
environment where a host makes write I/Os to a single application volume (A); see
Figure 22-9.
Figure 22-9 Start with simple application environment
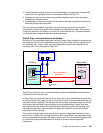
22.3.2 Establish connectivity to remote site
Now we add a distant site which has a storage disk subsystem (B), and we want to
interconnect both sites; see Figure 22-10 on page 256.
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
A
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
Primary
A
Host
Write I/O
Remote site
Local site