CHAPTER 2 V
R
4120A
Preliminary User’s Manual S15543EJ1V0UM
115
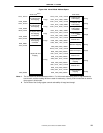
(9) xkseg (64-bit kernel mode, physical spaces)
When the KX = 1 in the Status register and bits 63 and 62 of the virtual address space are 11, the virtual address
space is called xkseg and selected as either of the following:
• Kernel virtual space xkseg, the current kernel virtual space; the virtual address is extended with the contents
of the 8-bit ASID field to form a unique virtual address
This space is referenced via TLB. Whether cache can be used or not is determined by bit C of each page’s
TLB entry.
• One of the four 32-bit kernel compatibility spaces, as described in the next section.
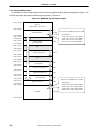
(10) 64-bit kernel mode compatible spaces (ckseg0, ckseg1, cksseg, and ckseg3)
If the conditions listed below are satisfied in Kernel mode, ckseg0, ckseg1, cksseg, or ckseg3 (each having 512
Mbytes) is selected as a compatible space according to the state of the bits 30 and 29 (two low-order bits) of the
address.
The KX bit of the Status register is 1.
Bits 63 and 62 of the 64-bit virtual address are 11.
Bits 61 to 31 of the virtual address are all 1.
(a) ckseg0
This space is an unmapped region, compatible with the 32-bit mode kseg0 space. The K0 field of the Config
register controls cacheability and coherency.
(b) ckseg1
This space is an unmapped and uncached region, compatible with the 32-bit mode kseg1 space.
(c) cksseg
This space is the current supervisor virtual space, compatible with the 32-bit mode ksseg space.
References to cksseg are mapped through TLB. Whether cache can be used or not is determined by bit C of each
page’s TLB entry.
(d) ckseg3
This space is the current supervisor virtual space, compatible with the 32-bit mode kseg3 space.
References to ckseg3 are mapped through TLB. Whether cache can be used or not is determined by bit C of
each page’s TLB entry.