Root Bridge Configuration 169
Prerequisites
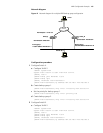
Before configuration, determine what roles the switches will play in the spanning
trees, that is, whether a switch will be the root, a branch, or a leaf in a spanning tree.
Configuring an
MST Region
Configuration procedure
Changes of MST region parameters, especially those of the VLAN mapping tables, can
cause MSTP to recalculate the spanning trees, creating network topology jitters across
the network. To reduce network topology jitters caused by configuration changes,
MSTP does not recalculate the spanning trees immediately in response to region
configuration changes. In fact, region configurations take effect only when you
perform any of the following operations:
■ Activate the new MST region settings by using the active region-configuration
command.
■ Enable MSTP by using the stp enable command.
Switches belong to the same MST region only when they have the same MST region
name, the same VLAN mapping table, and the same MST region revision level.
Table 142 Configure an MST region
Operation Command Description
Enter system view system-view —
Enter MST region view stp region-configuration —
Configure a name for the
MST region
region-name name Required
By default, the name of an MST
region is the MAC address of the
switch.
Configure the VALN
mapping table
instance instance-id vlan
vlan-list
Required
Both commands can be used to
configure a VLAN mapping table.
By default, all VLANs in an MST
region are mapped to MSTI 0.
vlan-mapping modulo
modulo
—
Configure the MSTP revision
level of the MST region
revision-level level Required
The default revision level of an
MST region is level 0.
Activate the configuration of
the MST region manually
active region-configuration Required
Display the configuration of
the MST region
check region-configuration Optional
Display the effective
configuration of the MST
region
display stp
region-configuration
You can execute this command in
any view.