40
Basics
1
Basic ATLAS Functions
This section describes the flow of translation work using translation memory,
which allows you to use ATLAS more effectively.
1.1 Flow of Automatic Translation
Translation by ATLAS can be divided into the following four basic steps.
1
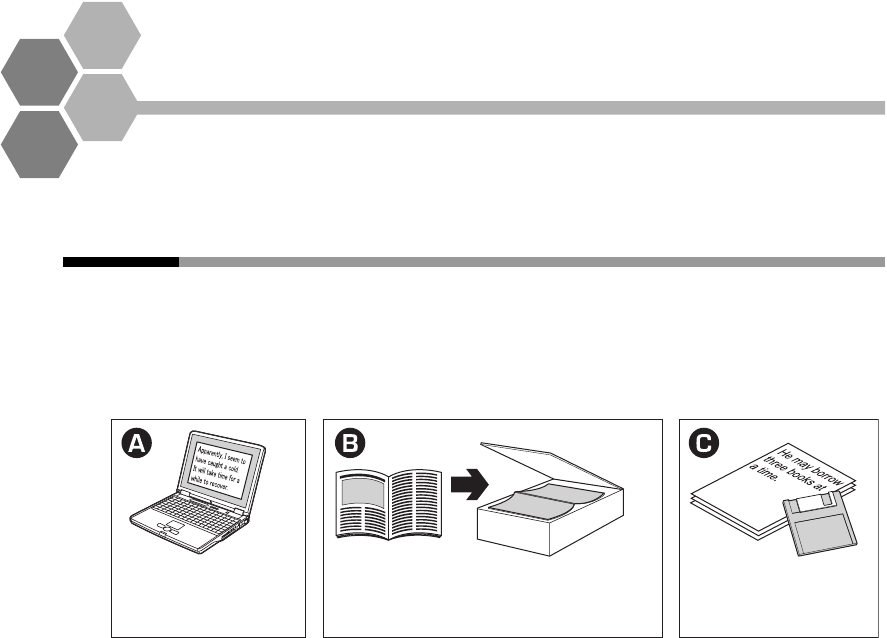
Preparing the source text
ATLAS translates electronic sentence data from the source language into the target
language.
2
Pre-editing
Before starting translation, review and pre-edit the source text. This step involves writing
original text that is optimized for translation. Pre-editing is an effective way to boost
translation quality.
Pre-editing includes:
● Defining the separation between sentences
● Re-writing complicated sentences into plain sentences
● Dividing long sentences into shorter sentences
● Correcting typos and syntax errors
3
Translation
ATLAS translates the source text into the target language. ATLAS has the following
functions.
● Translation of English text into Japanese text and vice versa.
● Translation Editor, Clipboard Translation, Web Translation functions, and Application
Translation.
● Use of the technical and User Dictionaries.
● Changing the translation environment style and the translation method.
4
Post-editing
Review and post-edit the translated text. This step involves checking and completing the
translation. Post-editing is an effective way to boost translation quality.
Post-editing includes:
● Checking the translated text for legibility
● Checking the translated text for syntax errors
Create the source text
by entering data in
your PC.
Read printed text using a scanner
and convert it into character data
using OCR software.
Prepare already
existing text.