More information
v Changing the RAID level (action)
v Changing the RAID level (SAS, SATA, HostRAID) (action)
v Changing the RAID level (enclosures) (action)
v Understanding logical-drive migration
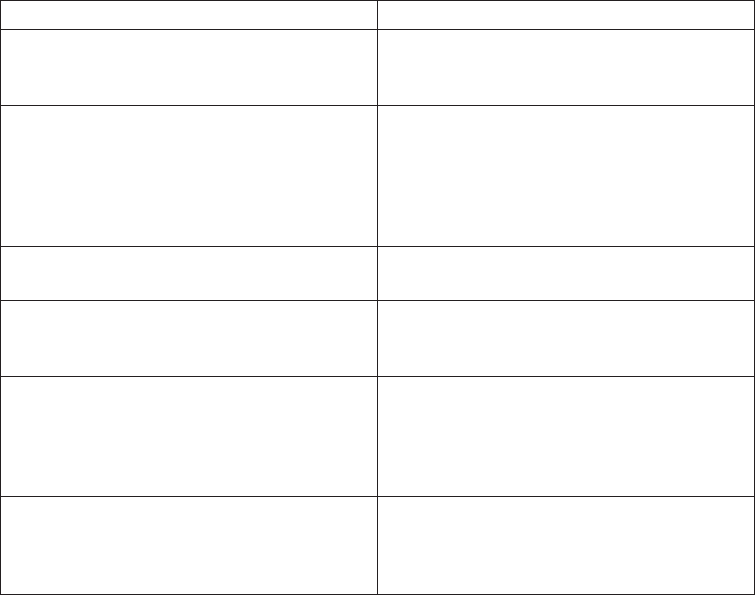
Application environment groups reference
Environment Applications
Groupware Lotus Notes
Microsoft Exchange
Other
Transaction processing DB2
Informix
Oracle
SQLServer
Sybase
Other
Decision support or data warehousing DB2 Informix Oracle SQLServer Sybase
Other
Thin client environments Citrix WinFrame or MetaFrame
Microsoft Terminal Server
Other
File server Novell NetWare
Microsoft Windows 2000
Microsoft Server 2003
Other network operating systems (for
example, OpenServer, Linux)
Web server Apache
Microsoft IIS
Netscape Commerce Server
Other
Understanding write-cache mode for physical drives
When using the write-cache-mode option, you can choose from two available
settings.
Write back
For the write back setting, the controller sends data to the physical drive for
storage. Subsequently, the physical drive sends a confirmation to the controller
before actually storing the data. Doing so increases performance, but also contains
an element of risk.
192 ServeRAID Manager Installation and User's Guide


















