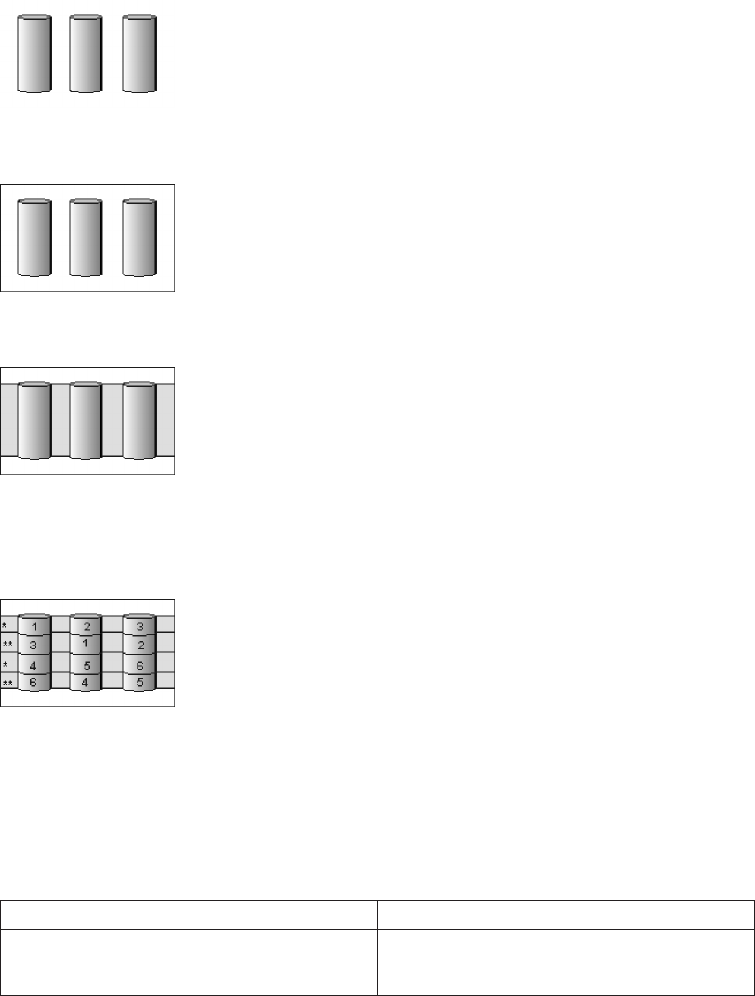
The following illustration is an example of a RAID level-1E logical drive.
RAID level-1 Enhanced example
Start with three physical drives.
Create an array using the physical drives.
Then create a logical drive within that array.
The data is striped across the drives, creating blocks. Notice that the stripe labeled
* is the data stripe and the stripe labeled ** is the copy of the preceding data
stripe. Also, notice that each block on the mirror stripe is shifted one drive.
With RAID level-1E, if one of the physical drives fails, the controller switches read
and write requests to the remaining functional drives in the RAID level-1E array.
Advantages and disadvantages
RAID level-1E offers the following advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages Disadvantages
v 100% data redundancy
v High performance
Allows only 50% of the physical drive
storage capacity to be used
More information
v Understanding RAID technology
v Understanding stripe-unit size
v Selecting a RAID level
v RAID level-0
v RAID level-1
v RAID level-5
Chapter 3. Using ServeRAID Manager 37


















