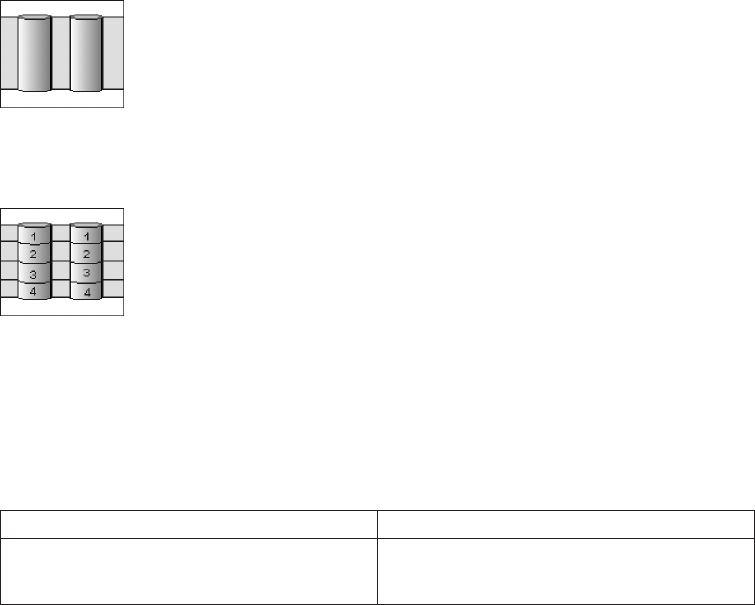
Then create a logical drive within that array.
The data is striped across the drives, creating blocks. Notice that the data on the
drive on the right is a copy of the data on the drive on the left.
With RAID level-1, if one of the physical drives fails, the controller switches read
and write requests to the remaining functional drive in the RAID level-1 array.
Advantages and disadvantages
RAID level-1 offers the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages Disadvantages
v 100% data redundancy
v High performance
Allows only 50% of the physical drive
storage capacity to be used
More information
v Understanding RAID technology
v Understanding stripe-unit size
v Selecting a RAID level
v RAID level-0
v RAID level-1 Enhanced
v RAID level-5
v RAID level-5 Enhanced
v RAID level-5EE
v RAID level-6
v RAID level-x0
v RAID volumes
v Software and hardware support of RAID levels
Understanding RAID level-1 Enhanced
RAID level-1 Enhanced (RAID level-1E) combines mirroring and data striping. This
RAID level stripes data and copies of the data across all of the drives in the array.
As with the standard RAID level-1, the data is mirrored, and the capacity of the
logical drive is 50% of the array capacity.
RAID level-1E has a similar profile to RAID level-1; it provides data redundancy
and high levels of performance, but the storage capacity is diminished. However,
RAID level-1E allows a larger number of physical drives to be used.
RAID level-1E requires a minimum of three drives and, depending upon the level
of firmware and the stripe-unit size, supports a maximum of 8 or 16 drives.
36 ServeRAID Manager Installation and User's Guide


















