data to be reconstructed more quickly if a physical drive in the array fails. With
such a configuration, you cannot share the spare drive with other arrays. If you
want a spare drive for any other array, you must have another spare drive for
those arrays.
RAID level-5EE requires a minimum of four drives and, depending upon the level
of firmware and the stripe-unit size, supports a maximum of 8 or 16 drives. RAID
level-5EE is also firmware-specific.
Note: For RAID level-5EE, you can have only one logical drive in an array.
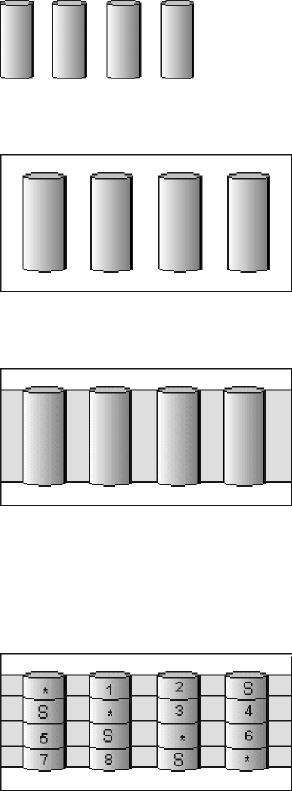
The following illustration is an example of a RAID level-5EE logical drive.
RAID level-5EE example
Start with four physical drives.
Create an array using all four physical drives.
Then create a logical drive within the array.
The data is striped across the drives, creating blocks in the logical drive. The
storage of the data parity (denoted by *) is striped, and it shifts from drive to
drive as it does in RAID level-5E. The spare drive (denoted by S) is interleaved
with the parity blocks, and it also shifts from drive to drive.
If a physical drive fails in the array, the data from the failed drive is reconstructed.
The array undergoes compaction, and the distributed spare drive becomes part of
the array. The logical drive remains RAID level-5EE.
42 ServeRAID Manager Installation and User's Guide


















