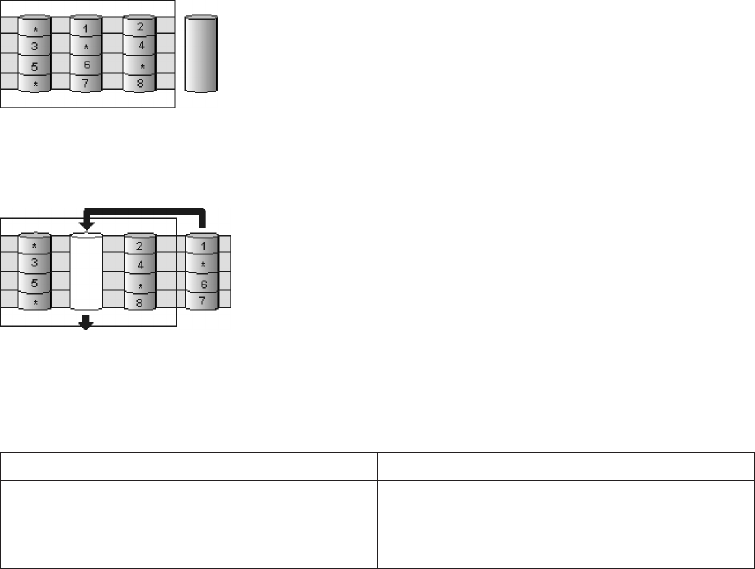
If a physical drive fails in the array, the data from the failed physical drive is
reconstructed onto the hot-spare drive.
Advantages and disadvantages
RAID level-5 offers the following advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages Disadvantages
v 100% data protection
v Offers more physical drive storage
capacity than RAID level-1 or level-1E
Lower performance than RAID level-1 and
level-1E
More information
v Understanding RAID technology
v Understanding stripe-unit size
v Selecting a RAID level
v RAID level-0
v RAID level-1
v RAID level-1 Enhanced
v RAID level-5 Enhanced
v RAID level-5EE
v RAID level-6
v RAID level-x0
v RAID volumes
Understanding RAID level-5 Enhanced
Note: This RAID level is not available on all controllers.
RAID level-5E is the same as RAID level-5 with a built-in spare drive. Like RAID
level-5, this RAID level stripes data and parity across all of the drives in the array.
RAID level-5E offers both data protection and increased throughput. When an
array is assigned RAID level-5E, the capacity of the logical drive is reduced by the
capacity of two physical drives in the array (one for parity and one for the spare).
Reading from and writing to four physical drives is more efficient than reading
from and writing to three physical drives and an idle hot spare. Therefore, RAID
level-5E provides a higher level of performance than RAID level-5.
Chapter 3. Using ServeRAID Manager 39


















