v RAID level-5 Enhanced
v RAID level-5EE
v RAID level-6
v RAID level-x0
v RAID volumes
Understanding RAID level-5
RAID level-5 stripes data and parity across all drives in the array.
RAID level-5 offers both data protection and increased throughput. When you
assign RAID level-5 to an array, the capacity of the array is reduced by the
capacity of one drive (for data-parity storage). RAID level-5 gives you higher
capacity than RAID level-1, but RAID level-1 offers better performance.
RAID level-5 requires a minimum of three drives and, depending upon the level of
firmware and the stripe-unit size, supports a maximum of 8 or 16 drives.
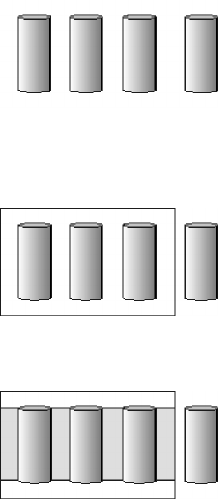
The following illustration is an example of a RAID level-5 logical drive.
RAID level-5 example
Start with four physical drives.
Create an array using three of the physical drives, leaving the fourth as a hot-spare
drive.
Then create a logical drive within that array.
The data is striped across the drives, creating blocks.
Notice that the storage of the data parity (denoted by *) also is striped, and it
shifts from drive to drive.
A parity block ( *) contains a representation of the data from the other blocks in
the same stripe. For example, the parity block in the first stripe contains data
representation of blocks 1 and 2.
38 ServeRAID Manager Installation and User's Guide


















