21555 Non-Transparent PCI-to-PCI Bridge User Manual 55
PCI Bus Transactions
When the initiator repeats the transaction using the same address, bus command, write data, and byte enables, then
the 21555 returns the appropriate target termination when ordering rules allow. Otherwise, the 21555 continues to
return target retry. The target terminations are listed in Table 13.
When the 21555 has a delayed completion to return to an initiator, and the initiator does not repeat the transaction
before the Master Time-Out Counter for that interface expires, it discards the delayed completion transaction.
When enabled to do so, the 21555 asserts SERR# on the initiator bus. The Master Time-Out Counter expiration
value is either 2
10
or 2
15
PCI clock cycles, programmable in the Chip Control 0 configuration register. The Master
Time-Out Counter is disabled when the Master Time-Out Disable bit in the Chip Control 0 configuration register is
zero.
5.4 Delayed Read Transactions
This section discusses the these Delayed Read Transactions:
• Section 5.4.1, “Nonprefetchable Reads” on page 56.
• Section 5.4.2, “Prefetchable Reads” on page 57.
• Section 5.4.3, “Prefetchable Read Transactions Using the 64-bit Extension” on page 57.
• Section 5.4.4, “Read Performance Features and Tuning Options” on page 57.
The 21555 uses delayed transactions when forwarding any type of read from one PCI interface to the other. Read
types are I/O, memory, memory read line, and memory read multiple.
Delayed transactions are also used for parallel ROM reads and CSR or configuration register reads that cause the
21555 to initiate a PCI read transaction, such as:
• CSR or configuration register read access that causes the 21555 to initiate a configuration read transaction.
• CSR read access that causes the 21555 to initiate an I/O read transaction.
The delayed read transaction protocol is similar to that of delayed write transactions, with the exception that 64-bit
transfers may be used for delayed-memory read transactions. When an I/O or memory read intended for the other
PCI bus is first initiated, the 21555 returns a target retry. The 21555 queues the transaction information if the
delayed transaction queue is not full and a transaction having the same address and bus command does not already
exist in the delayed transaction queue. This includes address, bus command, byte enables for nonprefetchable
reads.
Note: The byte enables are not checked when the 21555 decides whether to queue a delayed write
transaction.
When the transaction queued is a result of a CSR or configuration register read, the 21555 queues the appropriate
data based on the type of access desired, the address contained in the register, and the byte enables used for the data
register access. This phase of the delayed transaction is called a Delayed Read Request (DRR).
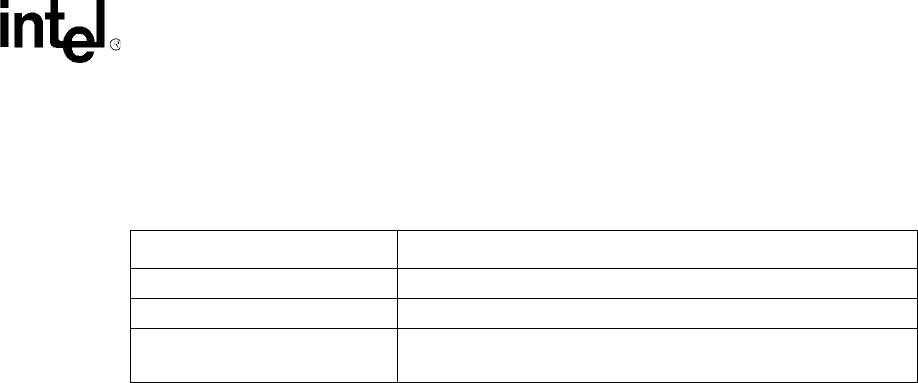
Table 13. Delayed Write Transaction Target Termination Returns
Target Bus Response Initiator Bus Response
TRDY# TRDY# and STOP# when multiple data phases are requested.
Target abort Target abort
Master abort
• TRDY# when Master Abort Mode bit = 0
• Target abort when Master Abort Mode bit = 1


















