E6581528
A-23
1
(2) Affects of leakage current across supply lines
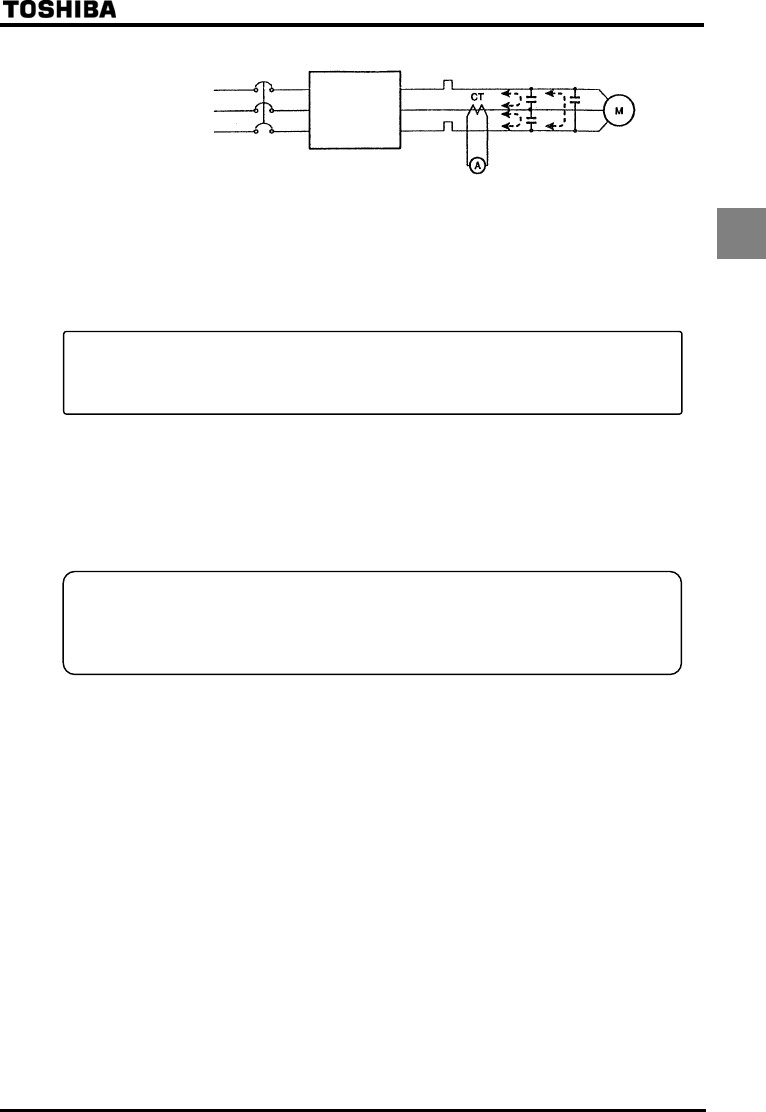
Power supply
inverter
Thermal relay
Leakage current path across wires
○
1
Thermal relays
The high frequency component of current leaking into electrostatic capacity between inverter output wires will
increase the effective current values and make externally connected thermal relays operate improperly. If the
motor cables are more than 50m long, external thermal relay may operate improperly with models having
motors of low rated current because the leakage current will be high in proportion to the motor rating.
Measures to be taken:
1. Use the electronic thermal overload built into the inverter.
The setting of the electronic thermal overload is done using parameter
or .
2. Reduce the inverter's PWM carrier frequency. However, that will increase the motor's acoustic noise.
The setting of PWM carrier frequency is done with the parameter
.
○
2
CT and ammeter
If a CT and ammeter are connected externally to measure inverter output current, the leakage current's high
frequency component may destroy the ammeter or CT. If the motor cables are more than 50m long, it will be
easy for the high frequency component to pass through the externally connected CT and be superimposed on
and burn the ammeter with models having motors of low rated current because the leakage current will increase
in proportion to the motor's rated current.
Measures to be taken:
1. Use a meter output terminal in the inverter control circuit.
The output current can be output on the meter output terminal (AM, FM). If the meter is connected, use an
ammeter of 1mAdc full scale or a voltmeter of 7.5Vdc-1mA full scale.
Inverter output terminal (FM) can be changed to 0-20mAdc (4-20mAdc) with
.
2. Use the monitor functions built into the inverter.
Use the monitor functions on the panel built into the inverter to check current values.