Scan Memory Commands
You can store up to 50,000 readings in non-volatile memory during
a scan. Readings are stored only during a scan and all readings are
automatically time stamped. If memory overflows (the
MEM annunciator
will turn on), a status register bit is set and new readings will overwrite
the first readings stored (the most recent readings are always preserved).
You can read the contents of memory at any time, even during a scan.
Reading memory is not cleared when you read it.
Each reading is stored with measurement units, time stamp, channel
number, and alarm status information. You can specify which information
you want returned with the readings using the FORMat:READing
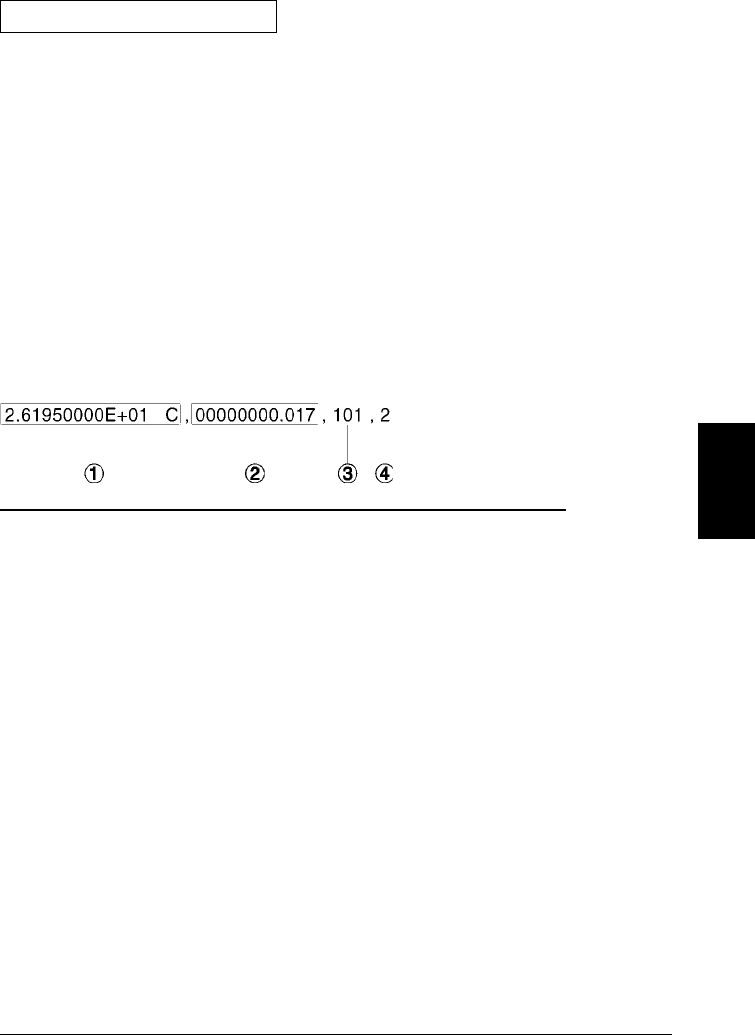
commands. The following is an example of a reading stored in memory
with all fields enabled (relative time is shown).
DATA:POINts?
Count the total number of readings (from all channels in the scan list)
currently stored in reading memory from a scan. Returns a value
between 0 and 50,000 readings.
DATA:REMove? <
num_rdgs>
Read and erase the specified number of readings from non-volatile
memory. The readings are erased from memory starting with the oldest
reading first. The purpose of this command is to allow you to periodically
remove readings from memory during a scan than would normally cause
reading memory to overflow (for example, during a scan with an infinite
scan count). The output from this command is affected by the
FORM:READ commands (see “Reading Format Commands” on page 231).
1 Reading with Units (26.195 °C)
2 Time Since Start of Scan (17 ms)
3 Channel Number
4 Alarm Limit Threshold Crossed
(0 = No Alarm, 1 = LO, 2 = HI)
5
Chapter 5 Remote Interface Reference
Scanning Overview
235


















