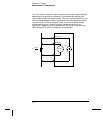
Sources of Error in Resistance Measurements
External Voltages Any voltages present in the system cabling or
connections will affect a resistance measurement. The effects of some of
these voltages can be overcome by using offset compensation (as described
on the previous page).
Settling Time Effects The internal
DMM has the ability to insert
automatic measurement settling delays. These delays are adequate for
resistance measurements with less than 200 pF of combined cable and
device capacitance. This is particularly important if you are measuring
resistances above 100 k
Ω. Settling due to RC time constant effects can
be quite long. Some precision resistors and multifunction calibrators
use large parallel capacitances (1000 pF to 0.1
µF) with high resistance
values to filter out noise currents injected by their internal circuitry.
Non-ideal capacitances due to dielectric absorption (soak) effects in
cables and other devices may have much longer settling times than
expected just by
RC time constants. Errors will be measured when
settling after the initial connection, after a range change, or when using
offset compensation. You may need to increase the channel delay time
before a measurement in these situations (for more information on
channel delay, see page 88).
High-Resistance Measurement Errors When you are measuring
large resistances, significant errors can occur due to insulation
resistance and surface cleanliness. You should take the necessary
precautions to maintain a “clean” high-resistance system. Test leads
and fixtures are susceptible to leakage due to moisture absorption in
insulating materials and “dirty” surface films. Nylon and
PVC are
relatively poor insulators (10
9
ohms) when compared to PTFE Teflon
insulators (10
13
ohms). Leakage from nylon or PVC insulators can easily
contribute a 0.1% error when measuring a 1 M
Ω resistance in humid
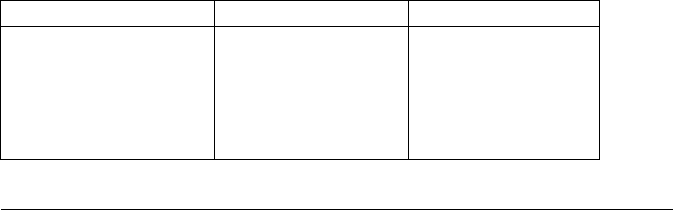
conditions. The table below shows several common insulating materials
and their typical resistances.
Insulating Material Resistance Range Moisture Absorbing
Teflon
®
(PTFE)
Nylon
PVC
Polystyrene
Ceramic
Glass Epoxy (FR-4, G-10)
Phenolic, Paper
1 T
Ω to 1 PΩ
1 GΩ to 10 TΩ
10 GΩ to 10 TΩ
100 GΩ to 1 PΩ
1 GΩ to 1 PΩ
1 GΩ to 10 TΩ
10 MΩ to 10 GΩ
N
Y
Y
N
N
Y
Y
Chapter 8 Tutorial
Measurement Fundamentals
372