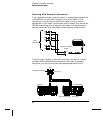
Signal Conditioning, Ranging, and Amplification Analog input
signals are multiplexed into the internal
DMM’s signal-conditioning
section – typically comprising switching, ranging, and amplification
circuitry. If the input signal is a dc voltage, the signal conditioner
is composed of an attenuator for the higher input voltages and a
dc amplifier for the lower input voltages. If the input signal is an
ac voltage, a converter is used to convert the ac signal to its equivalent
dc value (true
RMS value). Resistance measurements are performed by
supplying a known dc current to an unknown resistance and measuring
the dc voltage drop across the resistor. The input signal switching and
ranging circuitry, together with the amplifier circuitry, convert the
input to a dc voltage which is within the measuring range of the
internal
DMM’s analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
You can allow the instrument to automatically select the measurement
range using autoranging or you can select a fixed measurement range
using manual ranging. Autoranging is convenient because the instrument
automatically decides which range to use for each measurement based
on the input signal. For fastest scanning operation, use manual ranging
for each measurement (some additional time is required for autoranging
since the instrument has to make a range selection).
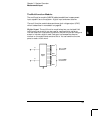
Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) The
ADC takes a prescaled
dc voltage from the signal-conditioning circuitry and converts it to digital
data for output and display on the front panel. The
ADC governs some of
the most basic measurement characteristics. These include measurement
resolution, reading speed, and the ability to reject spurious noise. There
are several analog-to-digital conversion techniques but they can be
divided into two types: integrating and non-integrating. The integrating
techniques measure the average input value over a defined time
interval, thus rejecting many noise sources. The non-integrating
techniques sample the instantaneous value of the input, plus noise,
during a very short interval. The internal
DMM uses an integrating
ADC technique.
You can select the resolution and reading speed from 6 digits (22 bits) at
3 readings per second to 4 digits (16 bits) at up to 600 readings per second.
The Advanced menu from the 34970A front panel allows you to control
the integration period for precise rejection of noise signals.
3
Chapter 3 System Overview
Measurement Input
61