Resistance Measurements
An ohmmeter measures the dc resistance of a device or circuit connected
to its input. Resistance measurements are performed by supplying a
known dc current to an unknown resistance and measuring the
dc voltage drop.
The internal
DMM offers two methods for measuring resistance:
2-wire and 4-wire ohms. For both methods, the test current flows from
the input
HI terminal through the resistor being measured. For 2-wire
ohms, the voltage drop across the resistor being measured is sensed
internal to the
DMM. Therefore, test lead resistance is also measured.
For 4-wire ohms, separate “sense” connections are required. Since no
current flows in the sense leads, the resistance in these leads does not
give a measurement error.
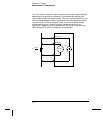
4-Wire Ohms Measurements The 4-wire ohms method provides the
most accurate way to measure small resistances. Test lead, multiplexer,
and contact resistances are automatically reduced using this method.
The 4-wire ohms method is often used in automated test applications
where long cable lengths, input connections, and a multiplexer exist
between the internal
DMM and the device-under-test.
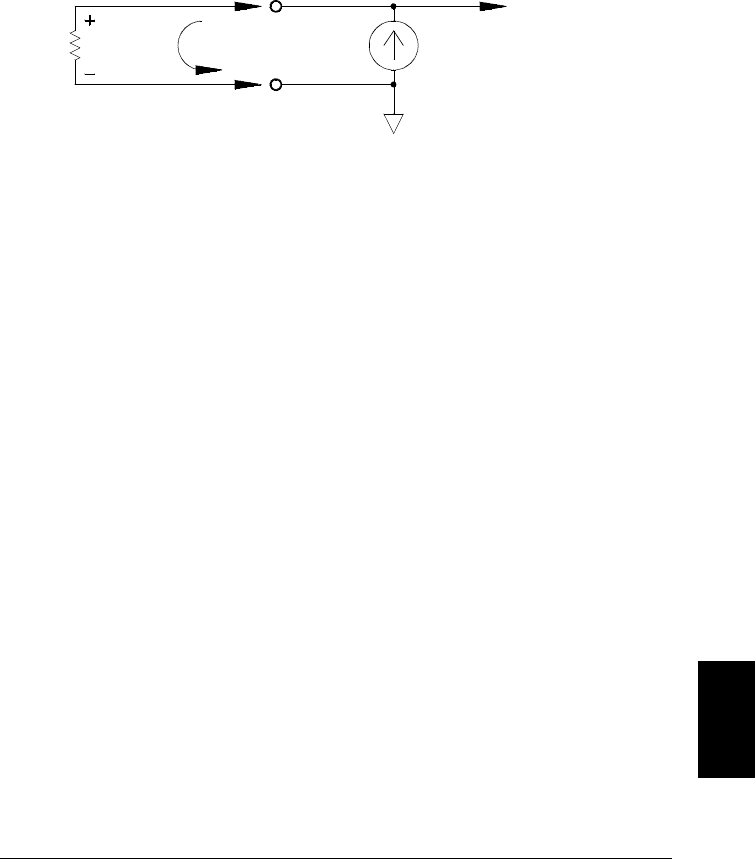
The recommended connections for 4-wire ohms measurements are
shown in the diagram on the following page. A constant current source,
forcing current I through unknown resistance R, develops a voltage
measured by a dc voltage front end. The unknown resistance is then
calculated using Ohm’s Law.
R
unknown
HI
LO
I
test
To Amplifier and
Analog-to-Digital
Converter
I
8
Chapter 8 Tutorial
Measurement Fundamentals
369