Shunt Impedance The insulation used for thermocouple wire and
extension wire can be degraded by high temperatures or corrosive
atmospheres. These breakdowns appear as a resistance in parallel with
the thermocouple junction. This is especially apparent in systems using
a small gauge wire where the series resistance of the wire is high.
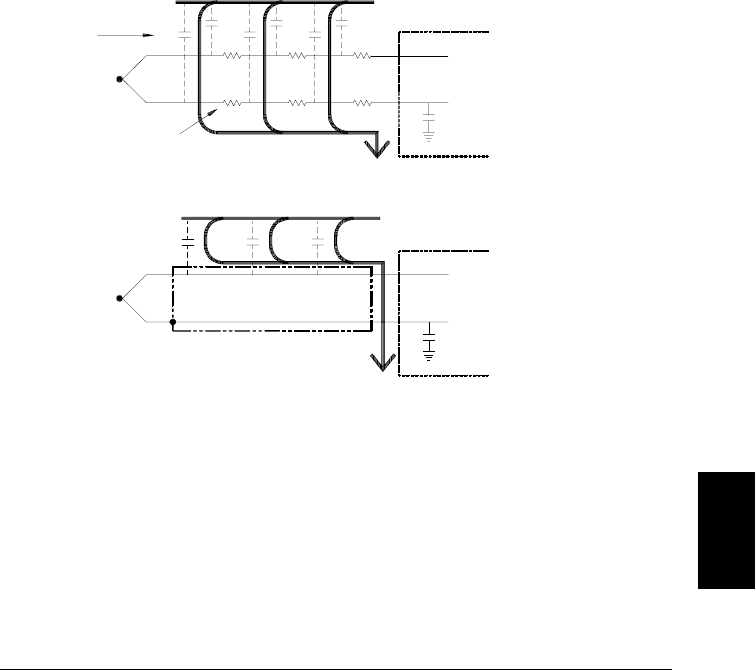
Shielding Shielding reduces the effect of common mode noise on a
thermocouple measurement. Common mode noise is generated by
sources such as power lines and electrical motors. The noise is coupled
to the unshielded thermocouple wires through distributed capacitance.
As the induced current flows to ground through the internal
DMM,
voltage errors are generated along the distributed resistance of the
thermocouple wire. Adding a shield to the thermocouple wire will shunt
the common mode noise to earth ground and preserve the measurement.
Common mode noise can dramatically affect the internal
DMM.
A typical thermocouple output is a few millivolts and a few millivolts of
common mode noise can overload the input to the internal
DMM.
Calculation Error An error is inherent in the way a thermocouple
voltage is converted to a temperature. These calculation errors are
typically very small compared to the errors of the thermocouple, wiring
connections, and reference junction (see page 345).
Distributed
Capacitance
Power Line
DMM
Distributed
Resistance
C C C
WITHOUT SHIELD
HI
LO
WITH SHIELD
C C C
HI
LO
DMM
C C C
R R R
Power Line
R R R
8
Chapter 8 Tutorial
Measurement Fundamentals
353
