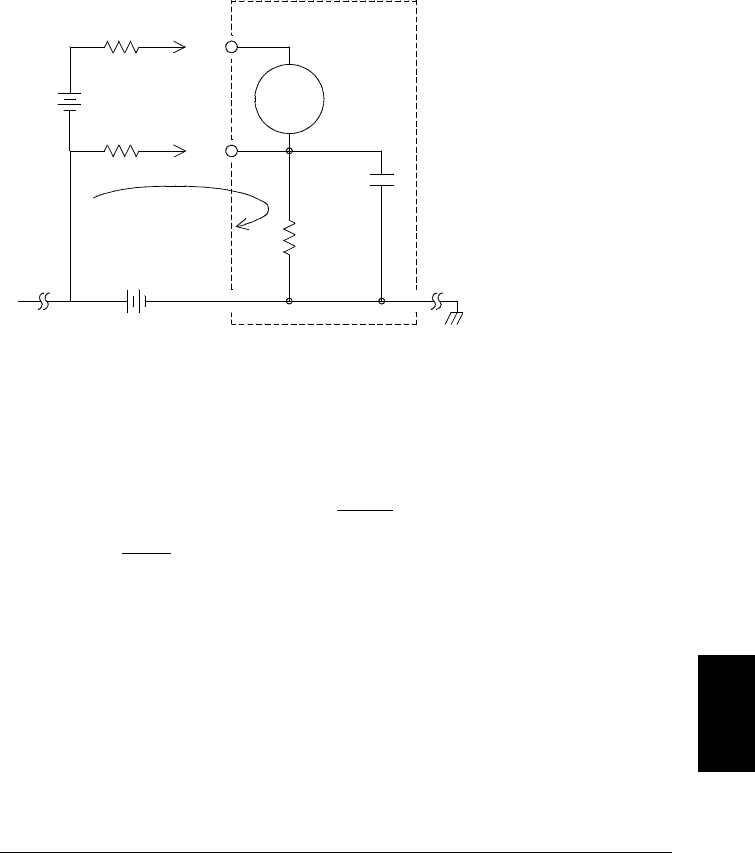
Noise Caused by Ground Loops When measuring voltages in circuits
where the internal
DMM and the device-under-test are both referenced
to a common earth ground, a ground loop is formed. As shown below,
any voltage difference between the two ground reference points (V
ground
)
causes a current to flow through the
LO measurement lead. This causes
an error voltage (V
L
) which is added to the measured voltage.
Where:
R
L
= Lead resistance
R
i
= DMM isolation resistance
C
i
= DMM isolation capacitance
V
ground
= Ground noise voltage
I = Current flow caused by V
ground
=
V
ground
R
L
+ Z
Z ≈ Z
Ci
=
1
2 π f
C
≈ 10 MΩ at 50 or 60 Hz
V
L
= I x R
L
To minimize ground loop errors:
• If V
ground
is a dc voltage, keep R
L
small compared to R
i
.
• If V
ground
is an ac voltage, keep R
L
small compared to Z, and set the
DMM’s integration time to 1 PLC or greater (see page 103 for a
discussion of integration time).
V
test
R
L
DMM
≈ C
i
250 pF
R
L
I
V
ground
R
i
>10 GΩ
LO
HI
8
Chapter 8 Tutorial
System Cabling and Connections
341


















