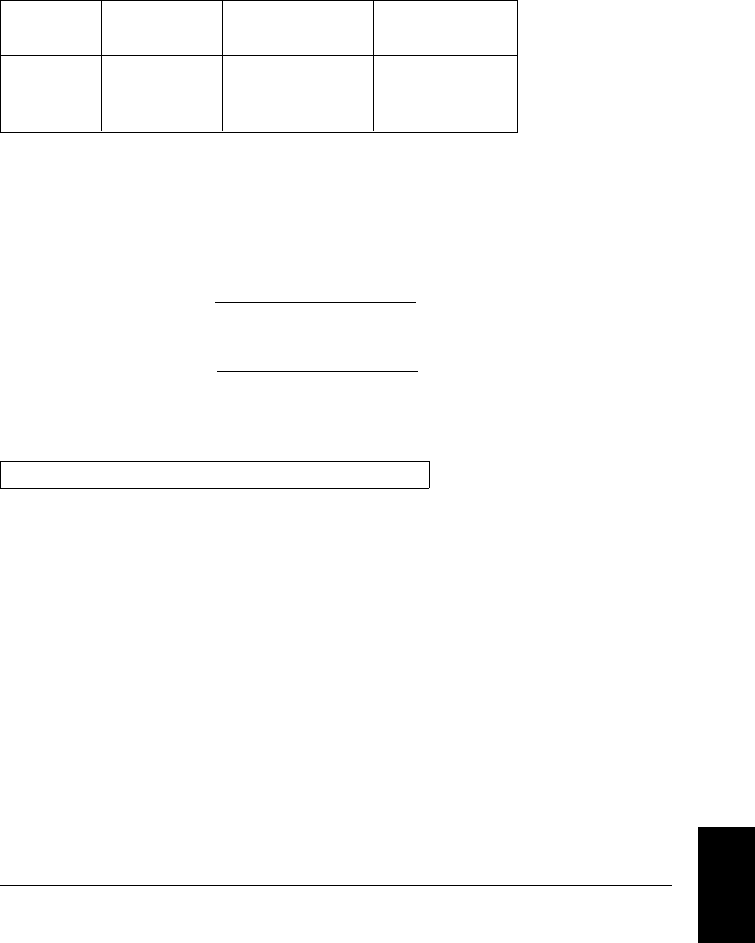
Understanding the “ % of range ” Error The range error compensates
for inaccuracies that result from the function and range you select.
The range error contributes a constant error, expressed as a percent of
range, independent of the input signal level. The following table shows
the range error applied to the
DMM’s 24-hour dc voltage specification.
Range Input Level
Range Error
(% of range)
Range
Error Voltage
10 Vdc
10 Vdc
10 Vdc
10 Vdc
1 Vdc
0.1 Vdc
0.0004
0.0004
0.0004
≤ 40 µV
≤ 40 µV
≤ 40 µV
Total Measurement Error To compute the total measurement error,
add the reading error and range error. You can then convert the total
measurement error to a “percent of input” error or a “ppm (part-per-
million) of input” error as shown below.
% of input error =
Total Measurement Error
Input Signal Level
× 100
ppm of input error =
Total Measurement Error
Input Signal Level
× 1,000,000
Example: Computing Total Measurement Error
Assume that a 5 Vdc signal is input to the DMM on the 10 Vdc range.
Compute the total measurement error using the 90-day accuracy
specification of
±(0.0020% of reading + 0.0005% of range).
Reading Error = 0.0020% x 5 Vdc = 100
µV
Range Error = 0.0005% x 10 Vdc = 50
µV
Total Error = 100
µV + 50 µV= ± 150 µV
=
± 0.0030% of 5 Vdc
=
± 30 ppm of 5 Vdc
9
Chapter 9 Specifications
To Calculate Total Measurement Error
415
