Eudora User Manual MAPI Overview
248
QUALCOMM Incorporated
MAPI Overview
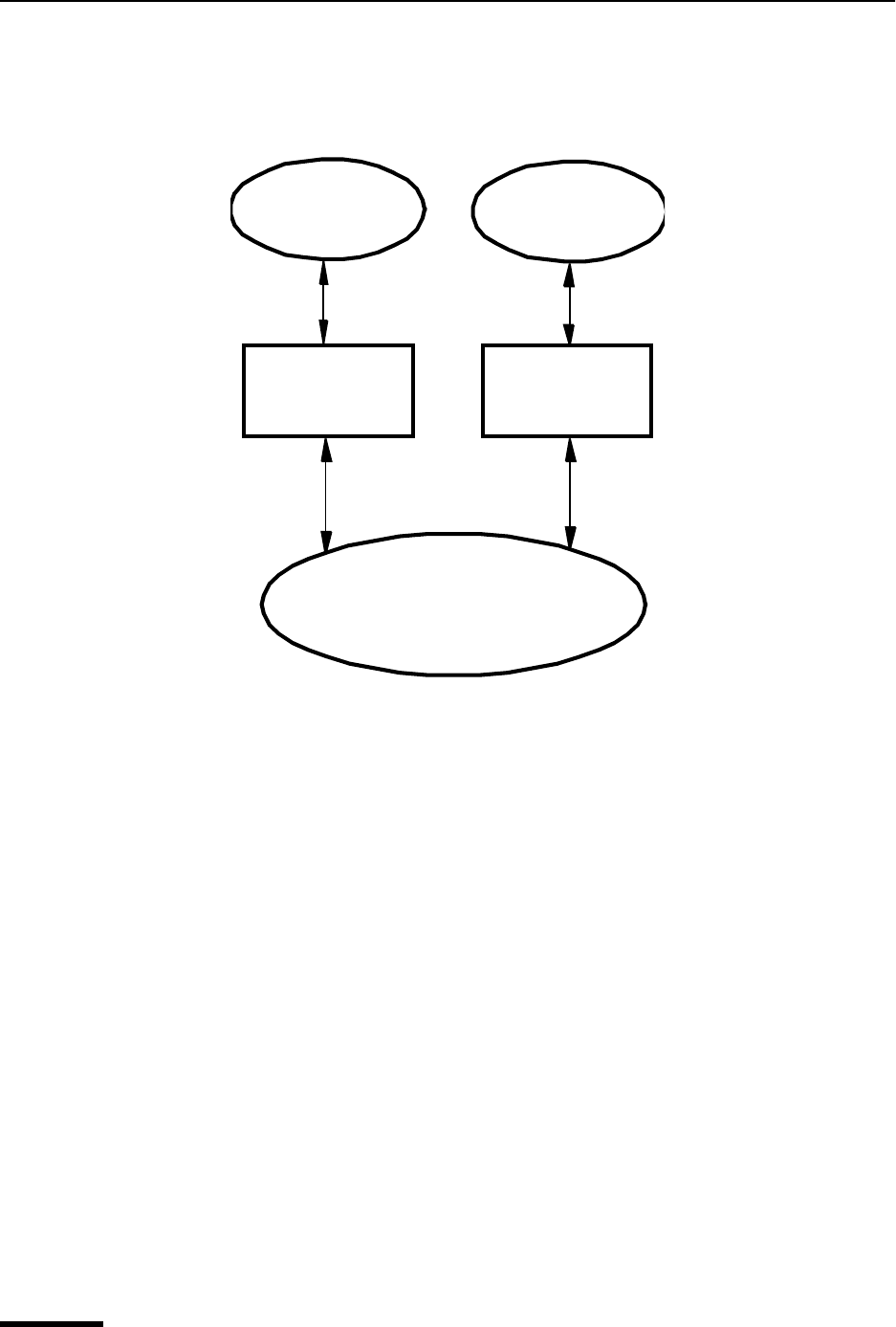
Let’s start with a picture:
A MAPI client application is any 16-bit or 32-bit Windows application that knows how to
access the standard MAPI messaging functions in a library known as a DLL (Dynamic
Link Library). The functions in the MAPI DLL allow a MAPI client application to transpar-
ently and generically access a MAPI service provider. A MAPI service provider is the
application that handles the receipt, transmission, and storage of messages. Examples of
MAPI client applications (“front-ends”) include Microsoft Word and Microsoft Excel. Exam-
ples of MAPI service providers (“back-ends”) include Microsoft Exchange and Microsoft
Fax.
All 16-bit client applications use the 16-bit MAPI.DLL and all 32-bit client applications use
the 32-bit MAPI32.DLL. The MAPI and MAPI32 DLLs are “twins” which contain the same
list of MAPI functions—they are parallel implementations of the 16-bit and 32-bit MAPI
functions. These DLLs are provided by Microsoft as standard components of Windows
95/98 and Windows NT. The MAPI DLLs are normally installed in the Windows 95/98
SYSTEM directory (SYSTEM32 for Windows NT).
When a MAPI client application wishes to send a document, it simply loads the appro-
priate MAPI library (DLL) and calls the defined MAPI functions. The MAPI DLL takes care
of routing the messaging and authentication requests to the appropriate MAPI service
provider application, displaying the address book user interface, and returning address
book and messaging data to the MAPI client application. The MAPI DLL also provides an
optional user interface for user authentication. For example, the user may need to supply
Eudora Pro
16-bit MAPI
client application
32-bit MAPI
client application
MAPI.DLL MAPI32.DLL