SCSI SCRIPTS 6-3
Each instruction consists of two or three 32-bit words. The first 32-bit
word is always loaded into the DMA Command (DCMD) and DMA Byte
Counter (DBC) registers, the second into the DMA SCRIPTS Pointer
Save (DSPS) register. The third word, used only by Memory Move
instructions, is loaded into the Temporary (TEMP) shadow register. In an
indirect I/O or Move instruction, the first two 32-bit opcode fetches are
followed by one or two more 32-bit fetch cycles.
6.2.1 Sample Operation
This sample operation describes execution of a SCRIPTS instruction for
a Block Move instruction.
• The host CPU, through programmed I/O, gives the DMA SCRIPTS
Pointer (DSP) register (in the Operating register file) the starting
address in main memory that points to a SCSI SCRIPTS program
for execution.
• Loading the DMA SCRIPTS Pointer (DSP) register causes the
LSI53C810A to request use of the PCI bus to fetch its first instruction
from main memory at the address just loaded.
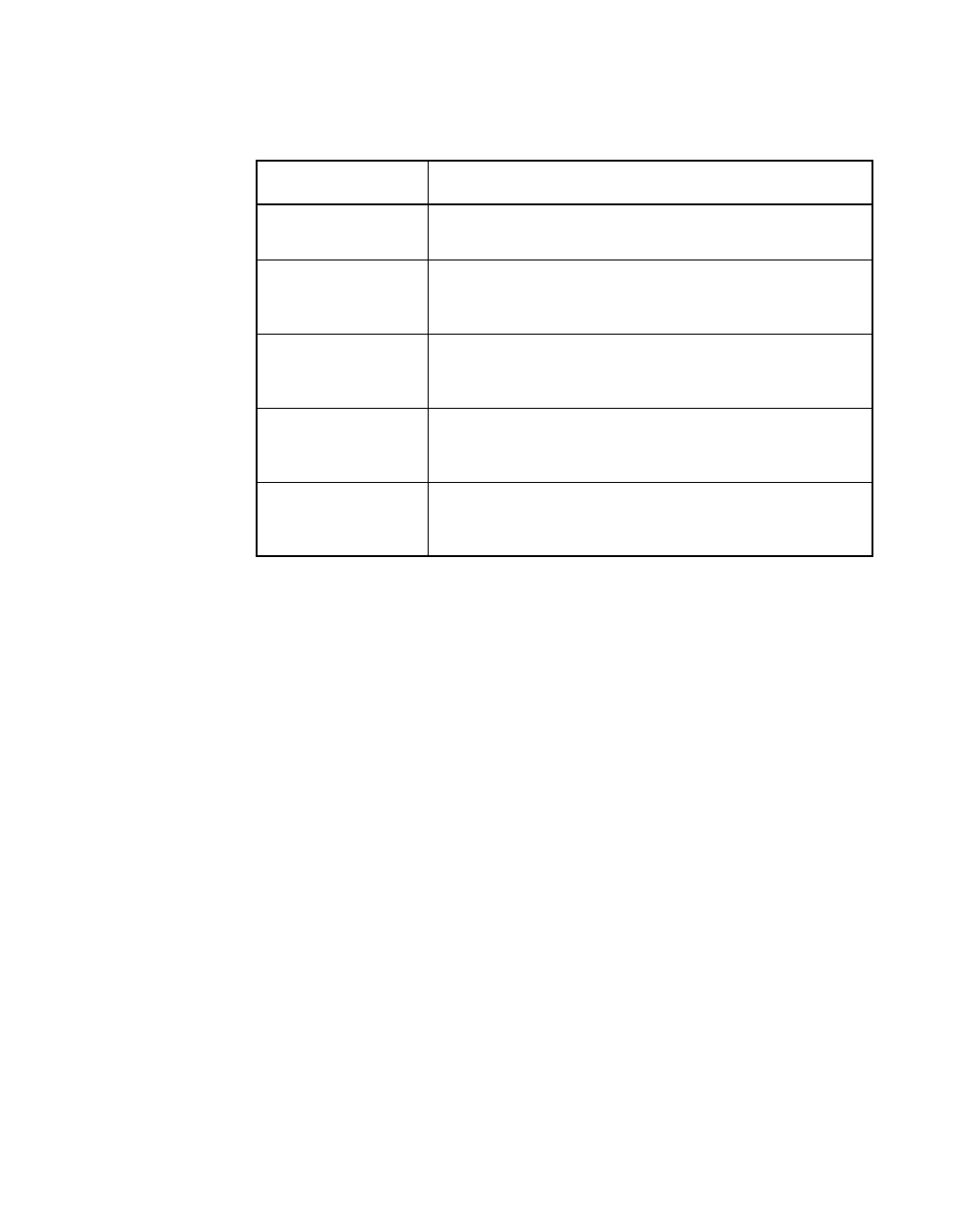
Table 6.1 SCRIPTS Instructions
Instruction Description
Block Move Block Move instruction moves data between the SCSI
bus and memory.
I/O or Read/Write I/O or Read/Write instructions cause the LSI53C810A to
trigger common SCSI hardware sequences, or to move
registers.
Transfer Control Transfer Control instruction allows SCRIPTS instructions
to make decisions based on real time SCSI bus
conditions.
Memory Move Memory Move instruction causes the LSI53C810A to
execute block moves between different parts of main
memory.
Load and Store Load and Store instructions provide a more efficient way
to move data to/from memory from/to an internal register
in the chip without using the Memory Move instruction.


















