DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS UNIT
10-4
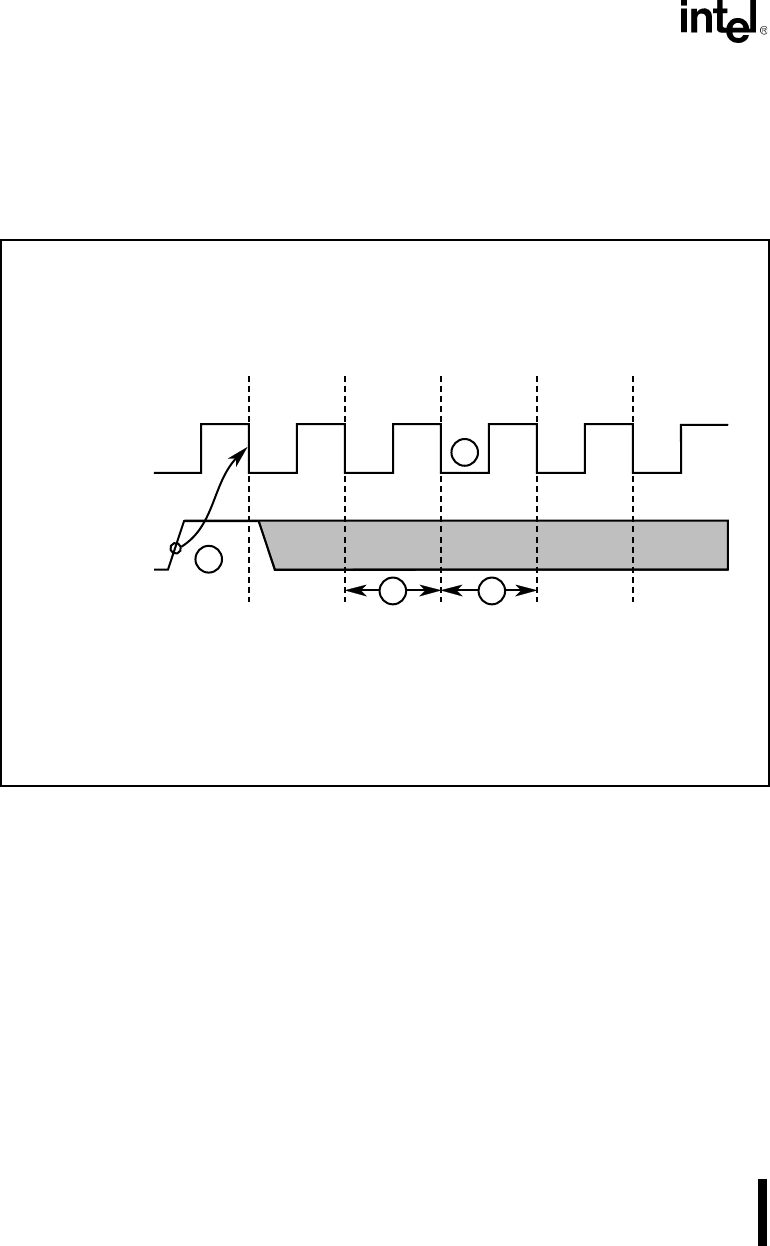
10.1.4 External Requests
External DMA requests are asserted on the DRQ pins. The DRQ pins are sampled on the falling
edge of CLKOUT. It takes a minimum of four clocks before the DMA cycle is initiated by the
BIU (see Figure 10-2). The DMA request is cleared four clocks before the end of the DMA cycle
(effectively re-arming the DRQ input).
Figure 10-2. DMA Request Minimum Response Time
External requests (and the resulting DMA transfer) are classified as either source-synchronized
or destination-synchronized. A source-synchronized request originates from the peripheral that is
sending data. For example, a disk controller in the process of reading data from a disk would use
a source-synchronized request (data would be moving from the disk to memory). A destination-
synchronized request originates from the peripheral that is receiving data. If a disk controller
were writing data to a disk, it would use a destination-synchronized request (data would be mov-
ing from memory to the disk). The type of synchronization a channel uses is programmable. (See
“Selecting Channel Synchronization” on page 10-18.)
DRQ
NOTES:
1. T
INVCL
: DMA request to clock low.
2. Synchronizer resolution time.
3. DMA unit priority arbitration and overhead.
4. Bus interface unit latches DMA request and decides to run DMA cycle.
4
2 3
T1 or
TW or
TI
T2 or
TW or
TI
T3 or
TW or
TI
T4 or
TI
T1
of
DMA
Cycle
1
A1528-0A


















