10-19
DIRECT MEMORY ACCESS UNIT
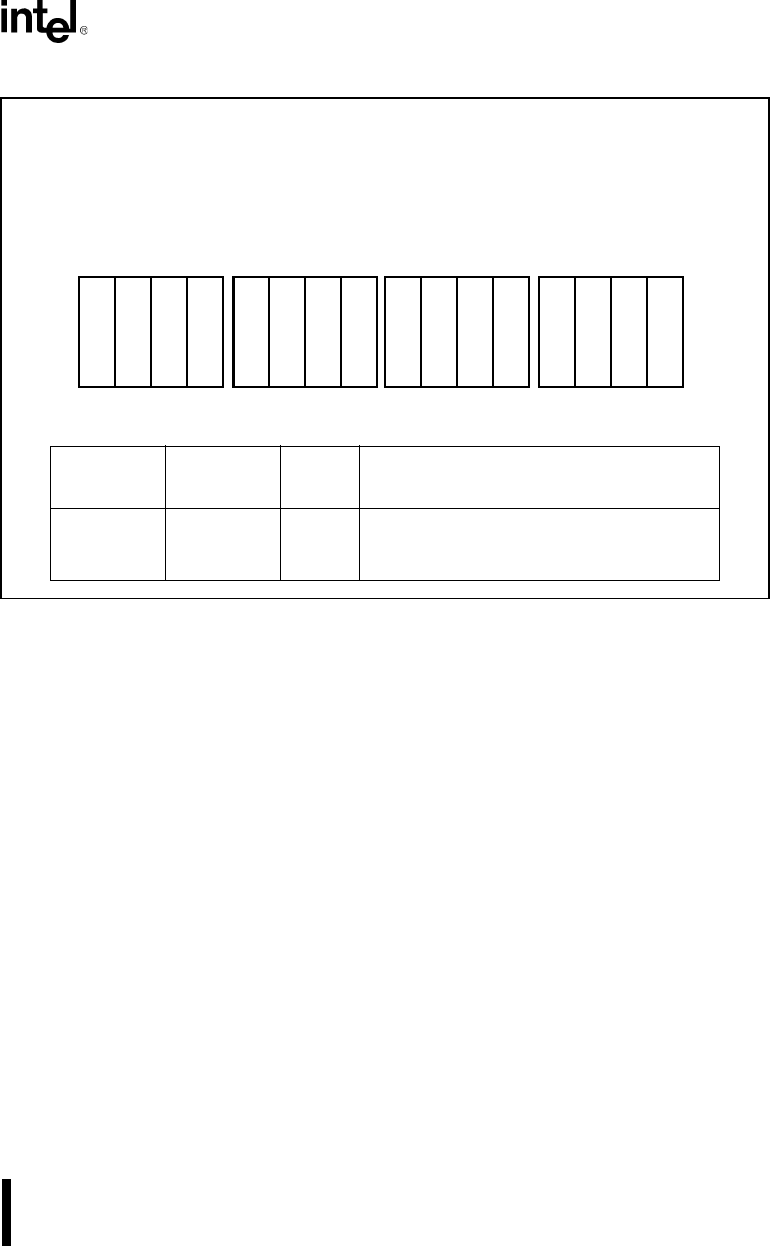
Figure 10-12. Transfer Count Register
The TC bit, when set, instructs the DMA channel to disarm itself (by clearing the STRT bit) when
the transfer count reaches zero. If the TC bit is cleared, the channel continues to perform transfers
regardless of the state of the Transfer Count Register. Unsynchronized (software-initiated) trans-
fers always terminate when the transfer count reaches zero; the TC bit is ignored.
10.2.1.7 Generating Interrupts on Terminal Count
A channel can be programmed to generate an interrupt request whenever the transfer count reach-
es zero. Both the TC bit and the INT bit in the DMA Control Register (Figure 10-11 on page
10-15) must be set to generate an interrupt request.
10.2.1.8 Setting the Relative Priority of a Channel
The priority of a channel is controlled by the Priority bit in the DMA Control Register (Figure
10-11 on page 10-15). A channel may be assigned either high or low priority. If both channels are
programmed to the same priority (i.e., both high or both low), the channels rotate priority.
Register Name: DMA Transfer Count
Register Mnemonic: DxTC
Register Function: Contains the DMA channel’s transfer count.
Bit
Mnemonic
Bit Name
Reset
State
Function
TC15:0 Transfer
Count
XXXXH Contains the transfer count for a DMA channel.
This value is decremented by one after each
transfer.
15 0
T
C
2
T
C
0
T
C
1
T
C
3
T
C
6
T
C
4
T
C
5
T
C
7
T
C
1
0
T
C
8
T
C
9
T
C
1
1
T
C
1
4
T
C
1
2
T
C
1
3
T
C
1
5
A1172-0A


















