2-27
OVERVIEW OF THE 80C186 FAMILY ARCHITECTURE
2.2.1.6 Processor Control Instructions
Processor control instructions (see Table 2-11) allow programs to control various CPU functions.
Seven of these instructions update flags, four of them are used to synchronize the microprocessor
with external events, and the remaining instruction causes the CPU to do nothing. Except for flag
operations, processor control instructions do not affect the flags.
2.2.2 Addressing Modes
The 80C186 Modular Core family members access instruction operands in several ways. Oper-
ands can be contained either in registers, in the instruction itself, in memory or at I/O ports. Ad-
dresses of memory and I/O port operands can be calculated in many ways. These addressing
modes greatly extend the flexibility and convenience of the instruction set. The following para-
graphs briefly describe register and immediate modes of operand addressing. A detailed descrip-
tion of the memory and I/O addressing modes is also provided.
2.2.2.1 Register and Immediate Operand Addressing Modes
Usually, the fastest, most compact operand addressing forms specify only register operands. This
is because the register operand addresses are encoded in instructions in just a few bits and no bus
cycles are run (the operation occurs within the CPU). Registers can serve as source operands, des-
tination operands, or both.
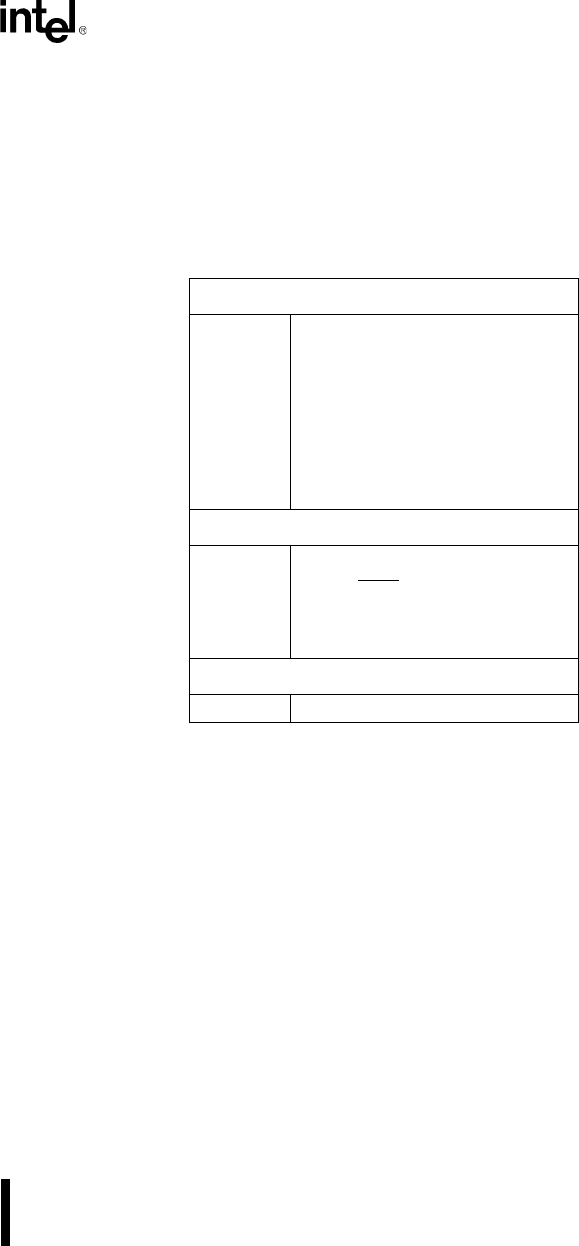
Table 2-11. Processor Control Instructions
Flag Operations
STC Set Carry flag
CLC Clear Carry flag
CMC Complement Carry flag
STD Set Direction flag
CLD Clear Direction flag
STI Set Interrupt Enable flag
CLI Clear Interrupt Enable flag
External Synchronization
HLT Halt until interrupt or reset
WAIT Wait for TEST
pin active
ESC Escape to external processor
LOCK Lock bus during next instruction
No Operation
NOP No operation