Security
Managing certificates
Note
Dummy Server Certificate: Used by the internal RADIUS server. This certificate is
present only to allow EAP-PEAP to work if the client chooses not to verify the server's
certificate. You should replace this with your own certificate for maximum security.
When a Web browser connects to the service controller using SSL, the service controller
sends only its own SSL certificate to the browser. This means that if the certificate has been
signed by an intermediate certificate authority, and if the Web browser only knows about the
root certificate authority that signed the public key certificate of the intermediate certificate
authority, the Web browser does not get the whole certificate chain it needs to validate the
identity of the service controller. Consequently, the Web browser issues security warnings.
To avoid this problem, make sure that you install the entire certificate chain when you install
a new certificate on the service controller.
Note An SNMP notification is sent to let you know when the service controller SSL certificate is
about to expire if you enable the Notifications option on the Service Controller >>
Management > SNMP page and then click Configure Notifications and enable the
Certificate about to expire notification under Maintenance.
Certificate usage
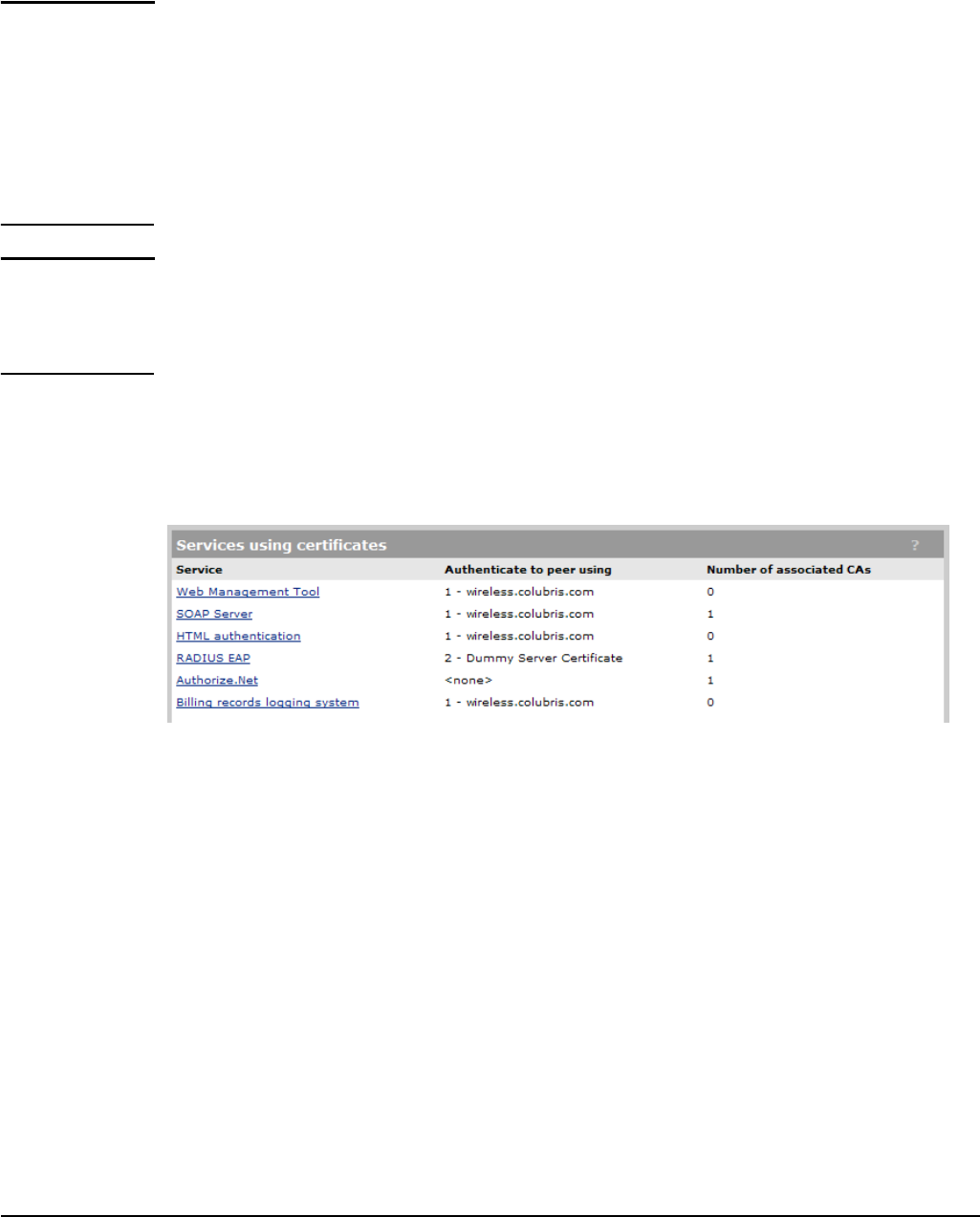
To see the services that are associated with each certificate, select Security > Certificate
usage. With the factory default certificates installed, the page will look like this:
Service
Name of the service that is using the certificate. To view detailed information on the
certificate select the service name.
Authenticate to peer using
Name of the certificate and private key. The service controller is able to prove that it has the
private key corresponding to the public key in the certificate. This is what establishes the
service controller as a legitimate user of the certificate.
Number of associated CAs
Number of CA certificates used by the service.
5-10