Working with controlled APs
Discovery of controlled APs
Discovery using an IP address: Enables the AP to find service controllers operating at a
specific IP address.
If only connectivity settings are provisioned, then the AP attempts to discover a service
controller using the same methods as for unprovisioned APs, namely:
UDP broadcast
DHCP (the AP must be configured as a DHCP client for this to work)
DNS
Tip For more information on provisioning APs, see Provisioning on page 3-31.
Discovery considerations
The following considerations must be made with respect to discovery:
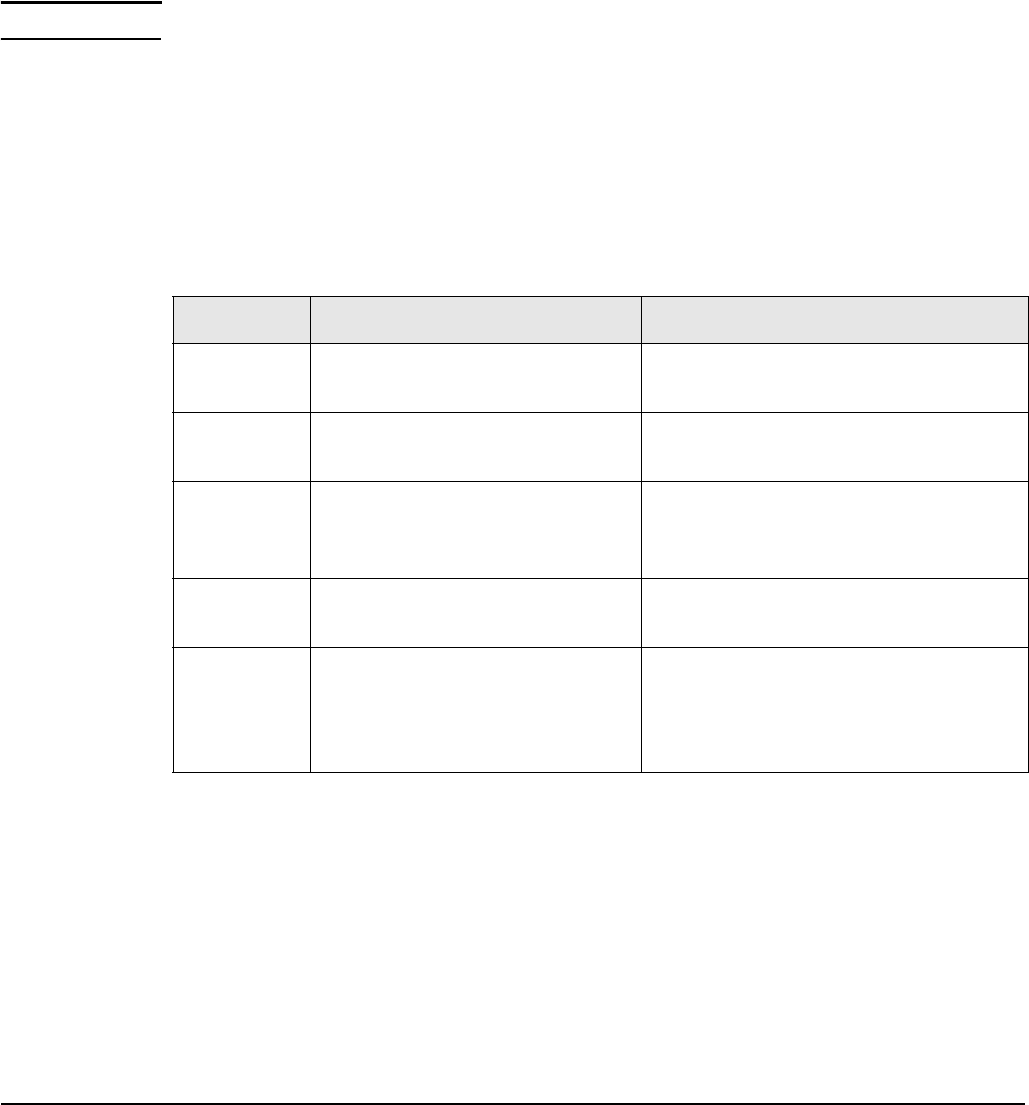
Firewall
If the network path between an AP and a service controller traverses a firewall the following
ports must be opened for management and discovery to work:
Protocol Open these ports Ports are used by
UDP Source and destination =
38212 (9544 hex).
Discovery protocol the AP uses to find
a service controller.
UDP Destination = 1194 (4AA hex). Management tunnel that is established
between an AP and a service controller.
TCP Source and destination = 1194
(4AA hex).
Software updates and certificate
exchanges (for the management
tunnel).
UDP Source and destination =
3001 (BB9 hex).
Client data tunnel.
UDP Source = 39064 (9898 hex) and
destination = 1800 (708 hex),
1812 (714 hex), 1813 (715 hex),
30840 (7878 hex).
Location aware. This is only necessary
if autonomous APs are using the
access-controlled (public access)
interface.
NAT
If the network path between an AP and a service controller implements NAT (network
address translation), discovery will only work if NAT functions on outbound traffic sent from
the AP to the service controller. If NAT operates in the other direction, discovery will fail.
3-12


















