Network configuration
Network address translation (NAT)
NAT security and static mappings
One of the benefits of NAT is that it effectively hides the IP addresses of all computers on the
internal network from the outside network. In some cases, however, it is useful to make a
computer on the internal network accessible externally. For example, a Web server or FTP
server.
Static NAT mapping addresses this problem. Static NAT mapping enables you to route
specific incoming traffic to an IP address on the internal network. For example, to support a
Web server, you can define a static NAT mapping to route traffic on TCP port 80 to an
internal computer running a Web server.
A static NAT mapping allows only one internal IP address to act as the destination for a
particular protocol (unless you map the protocol to a nonstandard port). For example, you
can run only one Web server on the internal network.
Note If you use a NAT static mapping to enable a secure (HTTPS) Web server on the internal
network on TCP port 443, remote access to the management tool is no longer possible,
as all incoming HTTPS requests are routed to the internal Web server and not to the
management tool. You can change the default management port (TCP 443) to an
alternate unused TCP port in this case.
If you create a static mapping, the firewall is automatically opened to accept the traffic.
However, this firewall rule is not visible on the Firewall configuration page.
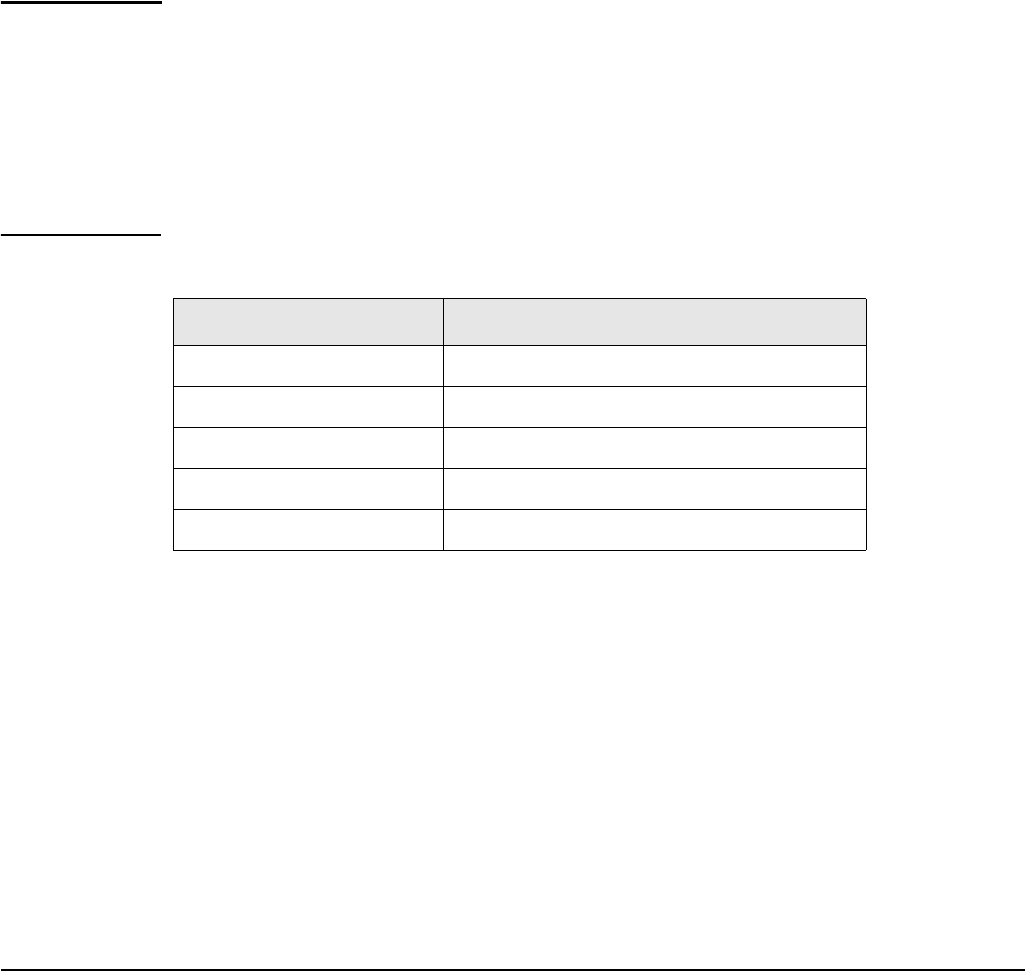
Common applications are affected by NAT as follows:
Application NAT
FTP (passive mode) Requires a static mapping to function.
FTP (active mode) Requires a static mapping to function.
NetMeeting Requires a static mapping to function.
Telnet Requires a static mapping to function.
Windows networking No effect
The service controller provides pre-configured static mappings for most common
applications, which you can enable as needed.
Most Web browsers use FTP in active mode. Some browsers provide a configuration option
that enables you to alter this. Use the following steps to change this behavior in Microsoft
Internet Explorer.
1. Select Tools > Internet options to open the Internet options dialog.
2. Select the Advanced tab.
3. Under Browsing, enable the Use Passive FTP for compatibility with some firewalls
and DSL modems checkbox.
10-24


















