User authentication
Key concepts
The AP can validate user login credentials using either the service controller or a third-party
RADIUS server. Access-controlled VSCs always use the service controller for all user
authentication tasks.
Authentication types
This section describes each authentication type.
802.1X authentication
Full support is provided for users with 802.1X or WPA / WPA2 client software that uses the
following:
EAP-TLS: Extensible Authentication Protocol Transport Layer Security.
EAP-TTLS: Extensible Authentication Protocol Tunnelled Transport Layer Security.
PEAP: Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol.
The group key can be changed at a specific interval.
Note For security reasons, use of 802.1X without enabling dynamic WEP encryption is not
recommended.
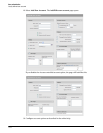
MAC-based authentication
Devices can be authenticated based on their MAC address. This is useful for authenticating
devices that do not have a Web browser (cash registers, for example).
There are two types of MAC-based authentication: global MAC and VSC-based MAC.
Global MAC VSC-based MAC
Supported on the service controller only. Supported on both service controller and AP.
Applies to both wired and wireless client
stations.
Applies to wireless client stations only.
Applies to all VSCs that have HTML-based
user authentication enabled. Authentication
server is defined on a per-VSC basis however.
Customizable on a per-VSC basis.
User credentials can be validated using either a local user accounts, a third-party RADIUS
server, or Active Directory. If more than one option is active, the local accounts are always
checked first.
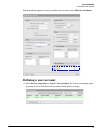
Global MAC
You can define global MAC-based authentication settings using the Colubris-AVPair value
string mac-address, which you must add to the RADIUS account for the service controller.
See MAC authentication on page 9-53.
7-3