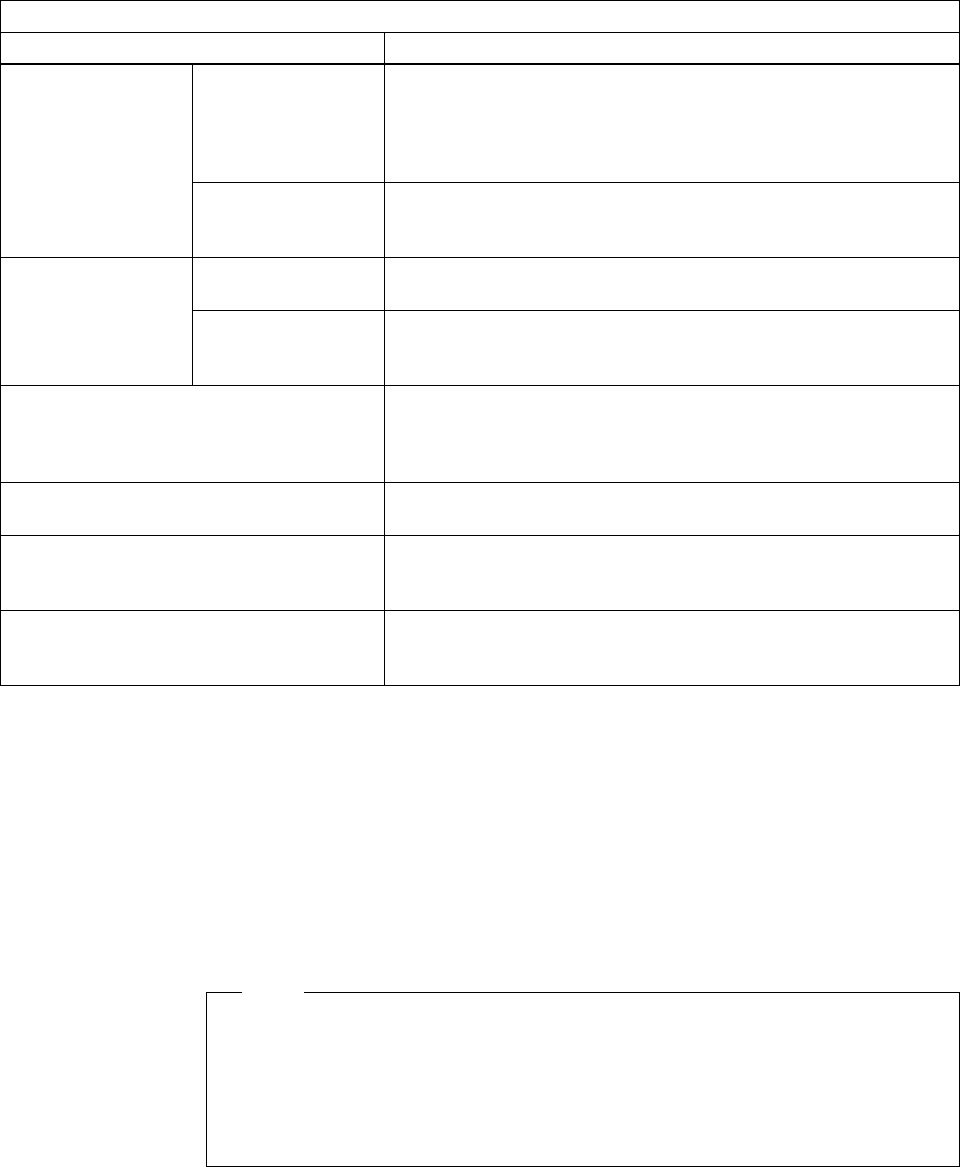
Table 33. MIB Structure for RFC 1513 - Token-Ring Extensions to the RMON MIB
Group Description
Token-ring
Statistics
Token-ring
MAC-layer
Statistics
This group collects ring error statistics and ring utilization from
the MAC layer. It samples MAC data and provides information
like MAC octets, MAC packets, beacon packets, line errors,
burst errors, token errors, lost frame errors, congestion errors,
etc.
Token-ring
Promiscuous
Statistics
This group collects statistics from non-MAC packets collected
like data packets, broadcast packets, multicast packets, etc.
History Token-ring
MAC-layer History
This group contains historical utilization and error statistics
collected from the MAC-layer.
Token-ring
Promiscuous
History
This group contains historical utilization and error statistics
collected from data packets.
Ring Station This group contains statistics and status information associated
with each token-ring station on the local ring. Information
provided includes number of active stations, current status of
ring, active monitor, etc.
Ring Station Order This group provides the order of the stations on monitored
rings.
Ring Station Configuration This group can manage the token-ring stations through active
means. It can download configuration information as well as
remove any station on a monitored ring.
Source Routing This group collects utilization statistics derived from source
routing information present in token-ring packets in a source
route bridging environment.
10.5.1.1 Statistics Group
The Statistics group provides a real-time view of the token-ring segment activity
as measured by the network probe attached to that segment. The statistics take
the form of free running counters that start from zero.
The Statistics group is divided into
MAC-Layer
and
Promiscuous
subgroups.
The MAC layer sits between the 802.2 LLC interface and the physical hardware.
MAC packets provide information that describes the physical condition of the
LAN.
Note
Promiscuous simply refers to non-MAC related objects such as data packets,
broadcast packets, multicast packets, etc. These packets must be collected
″promiscuously″. In other words, the device driver of the adapter must be
enabled to deliberately pick up those packets and pass them along to the
higher layers.
The Token-Ring MAC-Layer Statistics Group:
The MAC-layer statistics group
collects ring error statistics and ring utilization from the MAC layer. This group
samples MAC data and provides information like MAC octets, MAC packets,
beacon packets, line errors, burst errors, token errors, lost frame errors,
congestion errors, etc.
202 8260 Multiprotocol Intelligent Switching Hub


















