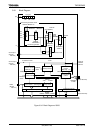
TMP92CM22
2007-02-16
92CM22-147
• Integer divider (N divider)
For example, when the f
C
= 39.3216 MHz, the input clock frequency = φT2, the
frequency divider N (BR0CR<BR0S3:0>) = 8, and BR0CR<BR0ADDE> = 0, the
baud rate in UART mode is as follows:
∗ Clock state
Clock gear: 1/1 (f
C
)
f
C
/32
8
= 39.3216 × 10
6
÷ 16 ÷ 8 ÷ 16 = 9600 (bps)
Note: The N + (16 − K)/16 division function is disabled and setting BR0ADD<BR0K3:0>
is invalid.
• N + (16 − K)/16 divider (UART mode only)
Accordingly, when f
C
= 31.9488 MHz, the input clock frequency = φT2, the
frequency divider N (BR0CR<BR0S3:0>) = 6, K (BR0ADD<BR0K3:0>) = 8, and
BR0CR<BR0ADDE> = 1, the baud rate is as follows:
* Clock state
Clock gear: 1/1 (f
C
)
f
C
/32
(16 − 8)
16
= 31.9488 × 10
6
÷ 32 ÷ (6 + ) ÷ 16 = 9600 (bps)
Table 3.9.3 show examples of UART mode transfer rates.
Additionally, the external clock input is available in the serial clock (Serial
channels 0 and 1). The method for calculating the baud rate is explained below:
• In UART mode
Baud rate = External clock input frequency ÷ 16
It is necessary to satisfy (External clock input cycle) ≥ 4/f
SYS
• In I/O interface mode
Baud rate = External clock input frequency
It is necessary to satisfy (External clock input cycle) ≥ 16/f
SYS
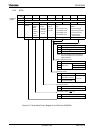
Baud rate =
÷ 16
8
16
÷ 16
6 +
Baud rate =