TMP92CM22
2007-02-16
92CM22-36
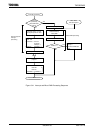
(2) Soft start function
In addition to starting the micro DMA function by interrupts, TMP92CM22 includes
a micro DMA software start function that starts micro DMA on the generation of the
write cycle to the DMAR register.
Writing “1” to each bit of DMAR register causes micro DMA once (If write “0” to each
bit, micro DMA doesn’t operate). At the end of transfer, the corresponding bit of the
DMAR register is automatically cleared to “0”.
Only one channel can be set for DMA request at once. (Do not write 1 to more than
one bit.)
When writing again 1 to the DMAR register, check whether the bit is 0 before
writing 1. If read “1”, micro DMA transfer isn’t started yet.
When a burst is specified by DMAB register, data is continuously transferred until
the value in the micro DMA transfer counter is “0” after start up of the micro DMA. If
execatee soft start during micro DMA transfer by interrupt source, micro DMA
transfer counter doesn’t change. Don’t use Read-modify-write instruction to avoid
writign to other bits by mistake.
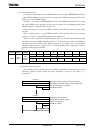
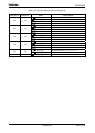
Symbol Name Address 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
DREQ7 DREQ6 DREQ5 DREQ4 DREQ3 DREQ2 DREQ1 DREQ0
R/W
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
DMAR
DMA
request
109H
(Prohibit
RMW)
1: DMA request in software
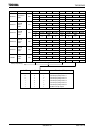
(3) Transfer control registers
The transfer source address and the transfer destination address are set in the
following registers. Data setting for these registers is done by an “LDC cr, r”
instruction.
Channel 0
DMAS0 DMA Source address register 0: only use LSB 24 bits.
DMAD0
DMA Destination address register 0: only use LSB 24 bits.
DMAC0
DMA Counter register 0: 1 to 65536.
DMAM0 DMA Mode register 0.
Channel 7
DMAS7
DMA Source address register 7.
DMAD7
DMA Destination address register 7.
DMAC7
DMA Counter register 7.
DMAM7
DMA Mode register 7.
8 bits
16 bits
32 bits