TMP92CM22
2007-02-16
92CM22-81
(iii) Example of register setting
To set the block address area 1 to 512 bytes from address 110000H, set the
register as follows.
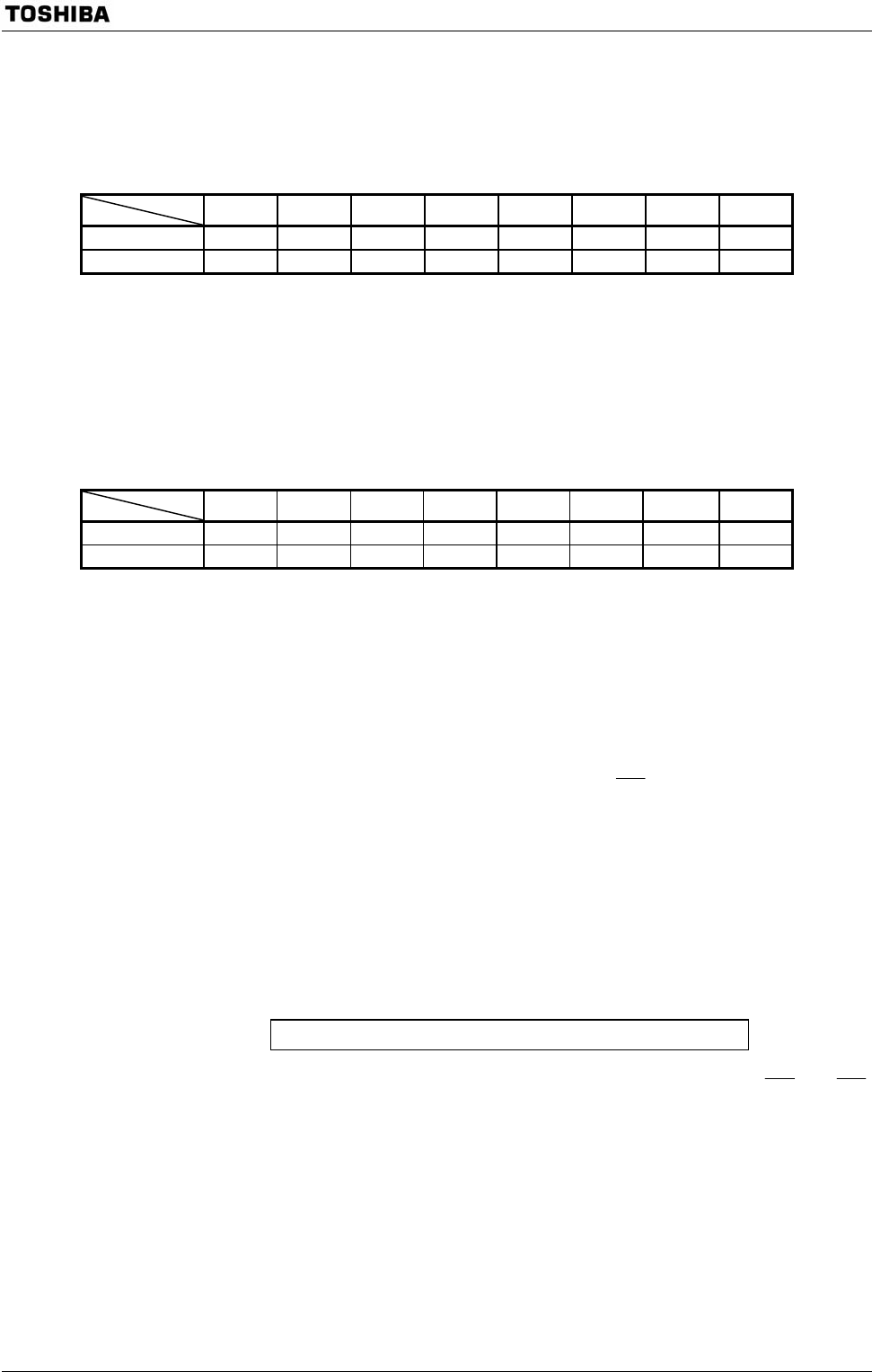
MSAR1 Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit symbol M1S23 M1S22 M1S21 M1S20 M1S19 M1S18 M1S17 M1S16
Setting value 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
M1S23 to M1S16 bits of the memory start address register MSAR1 correspond
with address A23 to A16.
A15 to A0 are cleared to “0”. Therefore setting MSAR1 to the above-mentioned
value specifies the start address of the block address area to address 110000H.
The start address is set as it is in the other block address areas.
MAMR1 Register
7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Bit symbol M1V21 M1V20 M1V19 M1V18 M1V17 M1V16 M1V15-9 M1V8
Setting value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
M1V21 to M1V16 and M1V8 bits of the memory address mask register
MAMR1 set whether address A21 to A16 and A8 are compared or not. Set the
register to “0” to compare, or to “1” not to compare. A23 and A22 are always
compared.
Setting the above-mentioned compares A23 to A9 with the values set as the
start addresses. Therefore 512 bytes of addresses 110000H to 1101FFH are set
as the block address area 1, and compared with the addresses on the bus. If the
compared result is a match, the chip select signal
CS1 is set to “low”.
The other block address area sizes are specified like this.
Similarly, A23 is always compared in block address areas 2 to 3. Whether A22
to A15 are compared or not is set to register.
Note: When the set block address area overlaps with the built-in memory area,
or both two address areas overlap, the block address area is processed
according to priority as follows.
Built-in I/O > Built-in memory > Block address area 0 >1 > 2 > 3 > CSEX
Also that any accessed areas outside the address spaces set by
CS0 to CS3
are processed as the CSEX space. Therefore, settings of CSEX apply for the
control of wait cycles, data bus width, etc.