Architecture
39
Chapter 4 Pipeline Architecture
4.1 Overview
The R3900 Processor Core executes instructions in five pipeline stages (F: instruction fetch; D: decode; E:
execute; M: memory access; W: register write-back). The five stages have the following roles.
F : An instruction is fetched from the instruction cache.
D : The instruction is decoded. Contents of the general-purpose registers are read. If the instruction
involves a branch or jump, the target address is generated. The coprocessor condition signal is latched.
E : Arithmetic, logical and shift operations are performed. The execution of multiple/divide instructions is
begun.
M : The data cache is accessed in the case of load and store instructions.
W : The result is written to a general register.
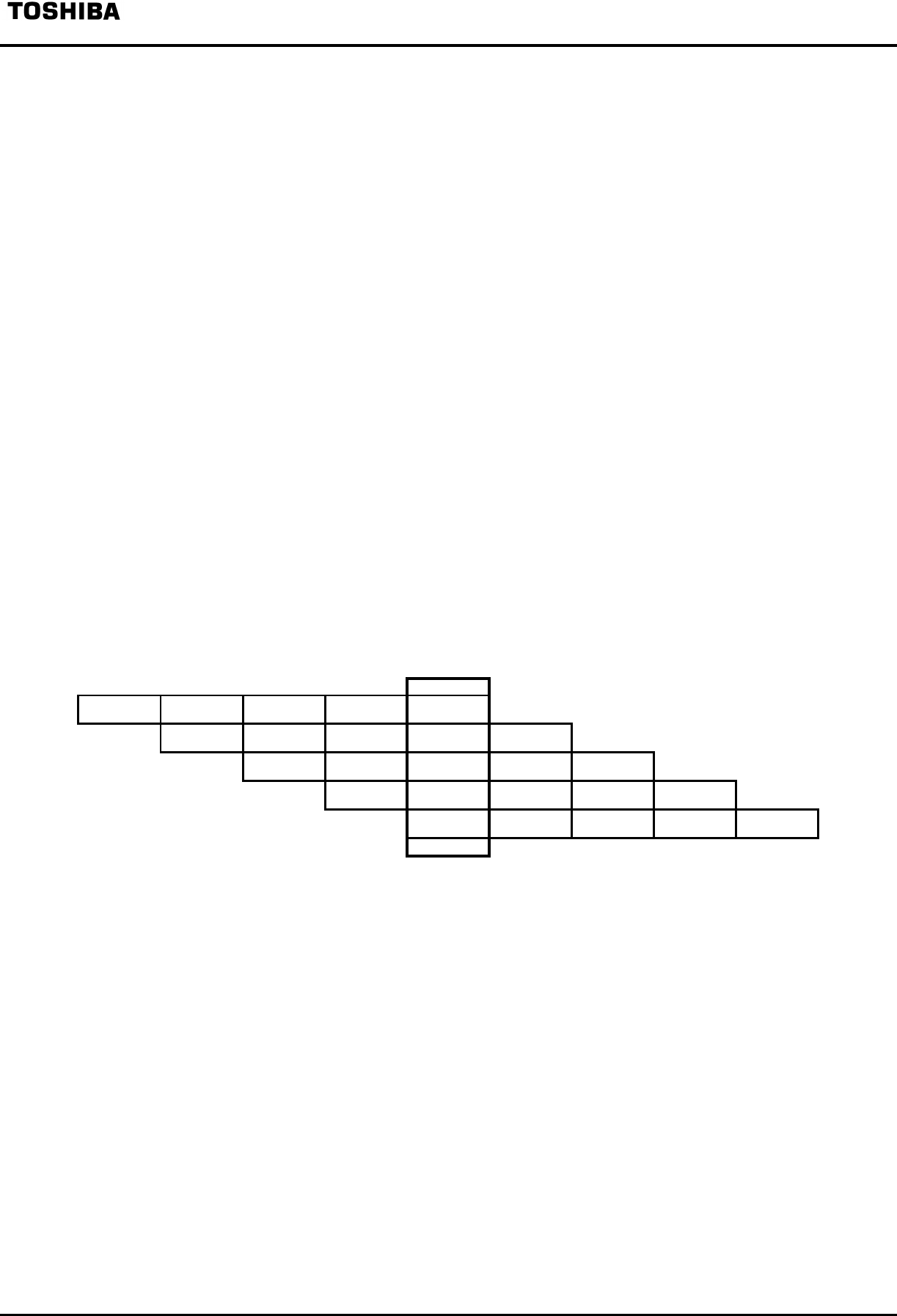
Each pipeline stage is executed in one clock cycle. When the pipeline is fully utilized, five instructions are
executed at the same time, resulting in an average instruction execution rate of one instruction per cycle as
illustrated in Figure 4-1.
F D E M W
F D E M W
F D E M W
F D E M W
F D E M W
Current CPU
cycle
Figure 4-1. Pipeline stages for executing R3900 Processor Core instructions


















