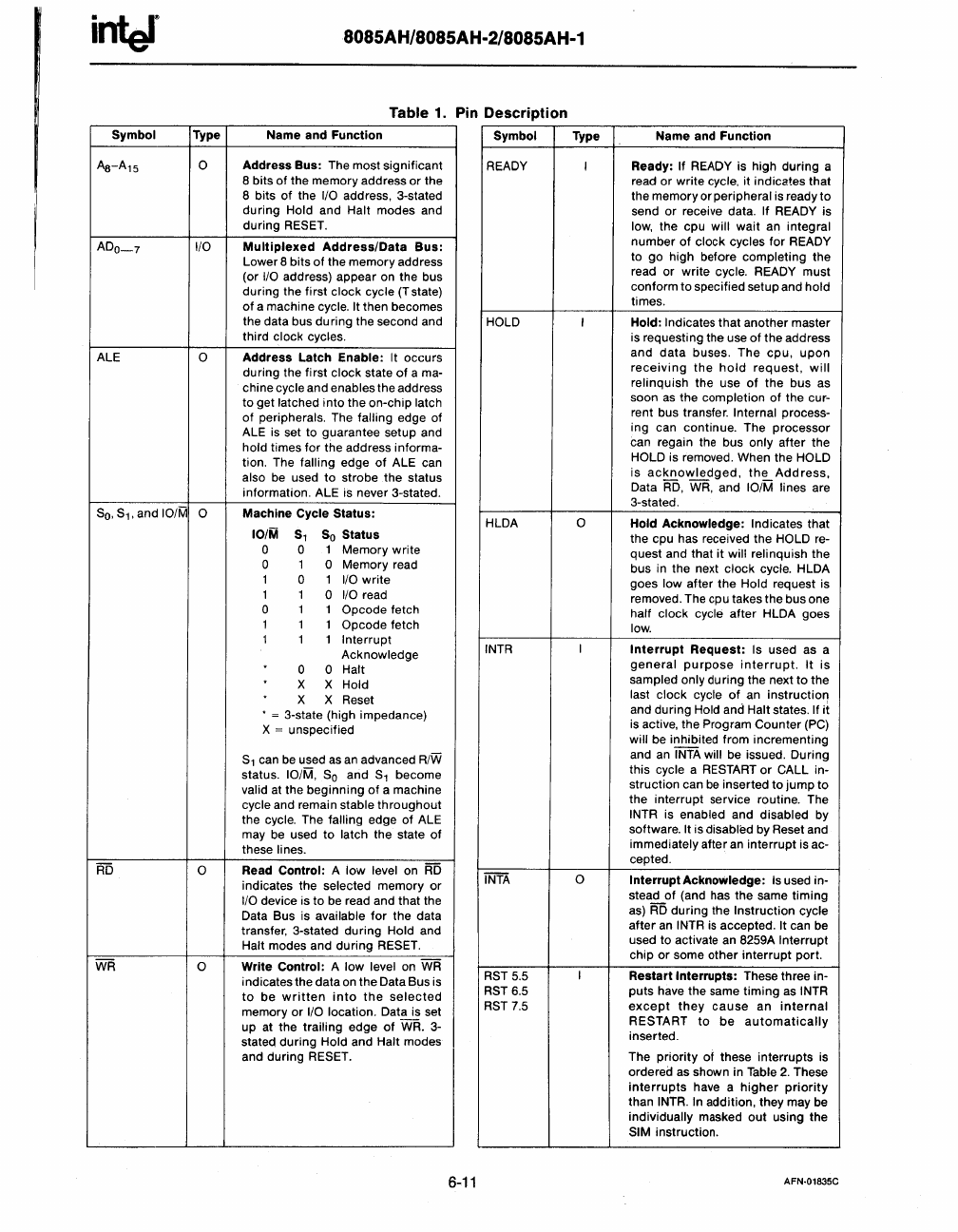
Symbol Type
o
ADO_7
I/O
ALE
o
So, S1,
and 10/M 0
RD
o
WR
o
8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1
Table
1.
Name and Function
Address Bus: The most significant
8 bits
of
the memory address or the
8 bits
of
the I/O address, 3-stated
during
Hold and Halt modes and
during
RESET.
Multiplexed Address/Data Bus:
Lower 8 bits
of
the memory address
(or
I/O
address) appear on the bus
during the first
clock cycle (Tstate)
of
a machine cycle. It then becomes
the data bus during the second and
third
clock cycles.
Address Latch Enable:
It occurs
during the first
clock state
of
a ma-
chine
cycle and enables the address
to get latched into the on-chip
latch
of
peripherals. The falling edge
of
ALE is set to guarantee setup and
hold times for the address informa-
tion. The
falling edge
of
ALE can
also
be
used to strobe the status
information. ALE is never 3-stated.
Machine Cycle Status:
10/M
S1
So
Status
0 0
1
Memory write
0 1 0 Memory read
1
0
1
I/O
write
1 1
0
I/O
read
0 1 1 Opcode fetch
1 1
1
Opcode fetch
1 1 1 Interrupt
Acknowledge
0 0
Halt
X
X
Hold
X X Reset
= 3-state (high impedance)
X
= unspecified
S1
can
be
used
as
an
advanced
R/Vii
status. IO/M,
SO
and
S1
become
valid at the beginning
of
a machine
cycle and remain stable
throughout
the cycle. The falling edge of ALE
may
be
used to latch the state
of
these lines.
Read Control: A
low level on
RD
indicates the selected memory or
I/O device is to
be
read and that the
Data Bus is
available
for
the data
transfer, 3-stated during
Hold and
Halt modes and during RESET.
Write Control: A low level
on
WR
indicates the data
on
the Data Bus is
to
be
written
into
the
selected
memory
or
I/O location. Data is set
up at the
trailing edge
of
WR.
3-
stated during Hold and Halt modes
and during
RESET.
Pin
Description
6-11
Symbol
READY
HOLD
HLDA
INTR
INTA
RST
5.5
RST
6.5
RST
7.5
Type
I
I
0
I
o
Name
and
Function
Ready:
If
READY
is high during a
read or write cycle, it indicates that
the memory or peripheral is ready
to
send
or
receive data. If READY is
low,
the cpu will wait an integral
number
of
clock cycles for READY
to go high before completing the
read or write cycle. READY must
conform to specified setup and
hold
times.
Hold:
Indicates that another master
is requesting the use
of
the address
and
data
buses. The
cpu,
upon
receiving
the
hold
request,
will
relinquish the use
of
the bus as
soon
as
the completion
of
the cur-
rent bus transfer.
Internal process-
ing can continue. The processor
can regain the bus
only after the
HOLD is removed. When the HOLD
is
acknowledged,
the
Address,
Data
RD,
WR,
and 10/M lines are
3-stated.
Hold Acknowledge:
Indicates that
the cpu has received the
HOLD re-
quest and that
it
will relinquish the
bus in the next
clock cycle. HLDA
goes
low after
the
Hold request is
removed. The cpu takes the bus one
half clock cycle after HLDA goes
low.
Interrupt Request: Is used as a
general
purpose
interrupt.
It
is
sampled
only during the next to the
last clock cycle
of
an instruction
and during
Hold and Halt states. If it
is active, the Program Counter
(PC)
will be inhibited from incrementing
and
an
INTA
will
be
issued. During
this
cycle a
RESTART
or
CALL in-
struction can
be
inserted to
jump
to
the interrupt service routine. The
INTR is enabled and disabled by
software.
It is disabled by Reset and
immediately after
an
interrupt is ac-
cepted.
Interrupt Acknowledge:
Is
used in-
stea~of
(and has the same timing
as)
RD
during the Instruction cycle
after
an
INTR
is
accepted. It can be
used to activate an 8259A
Interrupt
chip
or
some other interrupt port.
Restart
Interrupts: These three in-
puts have the same timing
as
INTR
except
they
cause
an
internal
RESTART
to
be
automatically
inserted.
The priority of these interrupts is
ordered as shown in
Table
2.
These
interrupts
have a
higher
priority
than INTR. In addition, they may
be
individually masked out using the
SIM instruction.
AFN·01835C