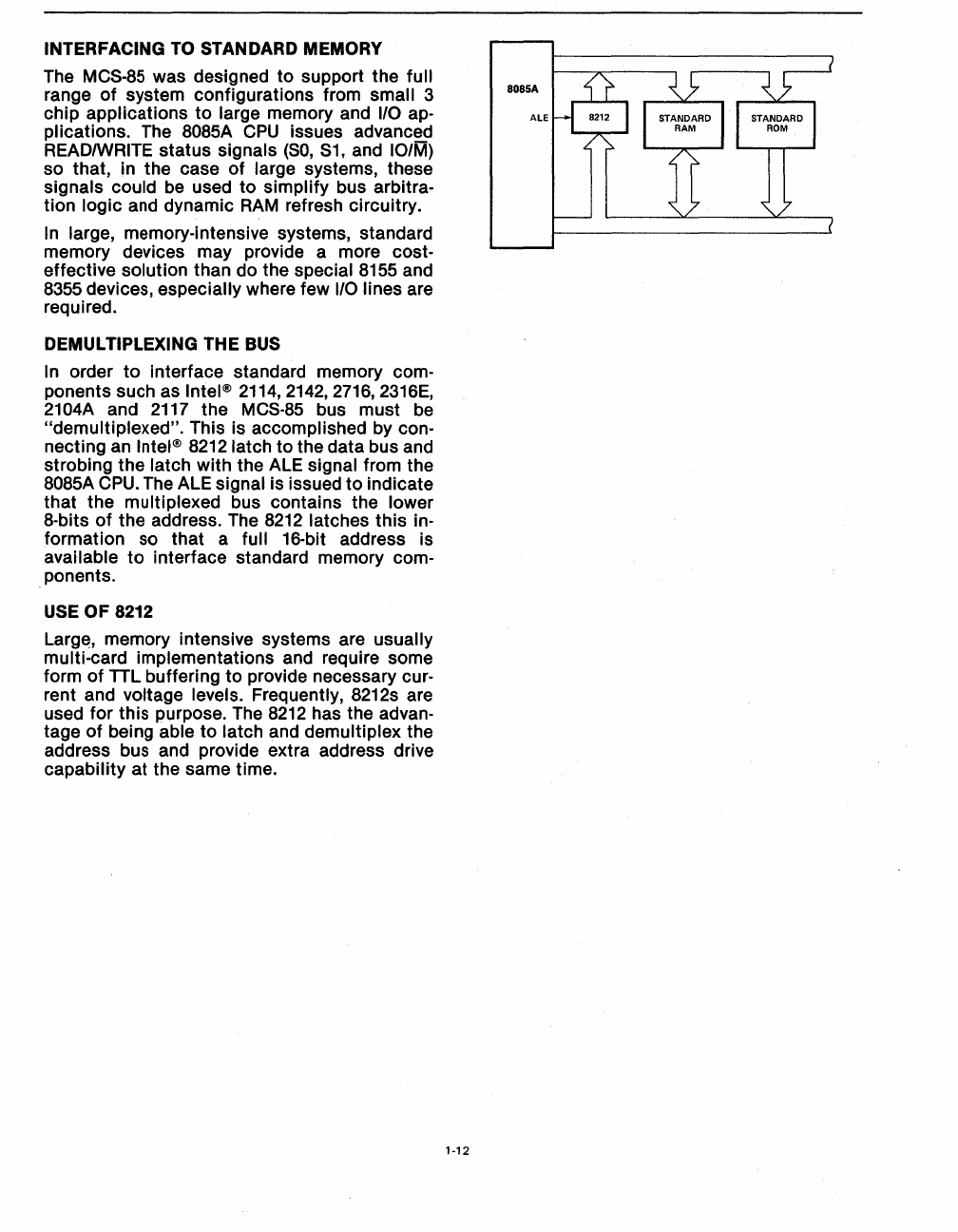
INTERFACING TO STANDARD MEMORY
The MC5-85 was designed
to
support the full
range
of
system configurations from small 3
chip applications
to
large memory and
110
ap-
plications. The
8085A
CPU
issues advanced
READIWRITE status signals
(SO,
51, and
101M)
so that, in the case
of
large systems, these
signals could
be
used
to
simplify bus arbitra-
tion logic and dynamic
RAM
refresh circuitry.
In
large, memory-intensive systems, standard
memory devices may provide a more cost-
effective solution than do the special 8155 and
8355 devices,
especially where few
110
lines are
required.
DEMULTIPLEXING THE BUS
In
order
to
interface standard memory com-
ponents such as
Intel® 2114,2142,2716, 2316E,
2104A and
2117
the MeS-85 bus must be
"demultiplexed". This is accomplished by con-
necting an
Intel®
8212
latch
to
the data bus and
strobing the latch with the ALE signal from the
8085A
CPU.
The ALE signal is issued
to
indicate
that the multiplexed bus contains the lower
8-bits
of
the address. The
8212
latches
this
in-
formation so that a
full 16-bit address is
available
to
interface standard memory com-
ponents.
USE
OF
8212
Larg~,
memory intensive systems are usually
multi-card implementations and require some
form
of
TIL
buffering
to
provide necessary cur-
rent and
voltage levels. Frequently, 8212s are
used
for
this purpose. The
8212
has the advan-
tage
of
being able
to
latch and demultiplex the
address bus and provide extra address drive
capability at the same time.
BOBSA
ALE
1-12