198
Intel
®
NetStructure™ 480T Routing Switch User Guide
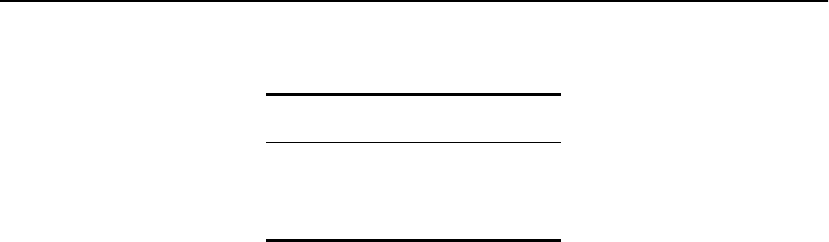
To change the relative route priority, use this command:
configure iproute priority [rip | bootp | icmp |
static | ospf-intra | ospf-inter | e-bgp | i-bgp |
ospf-extern1 | ospf-extern2] <priority>
IP Multinetting
IP multinetting is used in
many legacy IP networks
to overlap multiple subnets
onto the same physical
segment. Due to the
resulting constraints in
troubleshooting and
bandwidth limitations, we
recommend that
multinetting be used as a
transitional tool, and not
as a long-term network
design strategy.
On the 480T routing switch, each subnet is represented by a
different VLAN, and each of those VLANs has its own IP address.
All of the VLANs share the same physical ports. The switch routes
IP traffic from one subnet to another, all within the same physical
ports.
These rules and comments apply when you are configuring IP
multinetting:
• Multiple VLANs share the same physical ports; each of the
VLANs is configured with an IP address.
• A maximum of four subnets (or VLANs) on multinetted ports is
recommended.
• All VLANs used in the multinetting group must share the same
port assignment.
• One VLAN is configured to use an IP protocol filter. This is
considered the
primary VLAN interface for the multinetted
group.
• The secondary multinetted VLANs can be exported using the
export direct command.
• The FDB aging timer is automatically set to 3,000 seconds (50
minutes).
• If you are using a UDP or DHCP relay function, only the
primary
VLAN configured with the IP protocol filter is able to service
these requests.
• The VLAN
default should not be used for multinetting.
OSPFExtern2 3300
BOOTP 5000
Table 12.1: Relative Route Priorities (continued)
Route Origin Priority


















